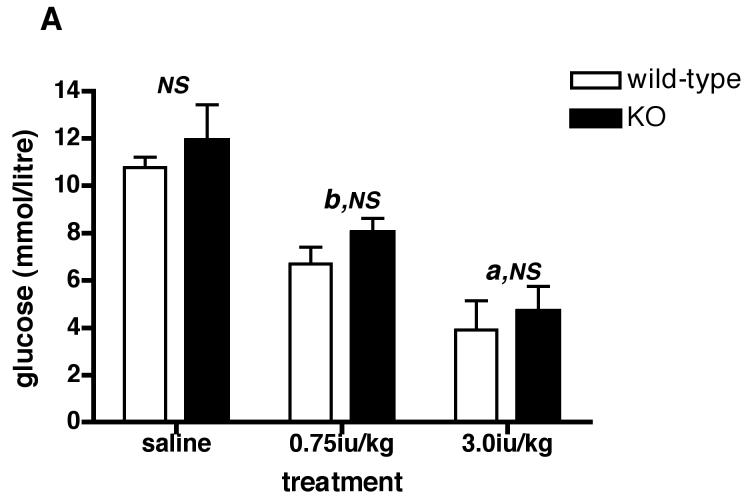
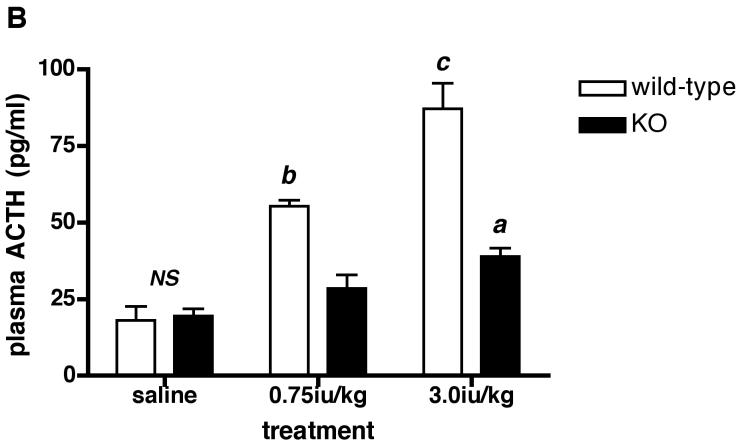
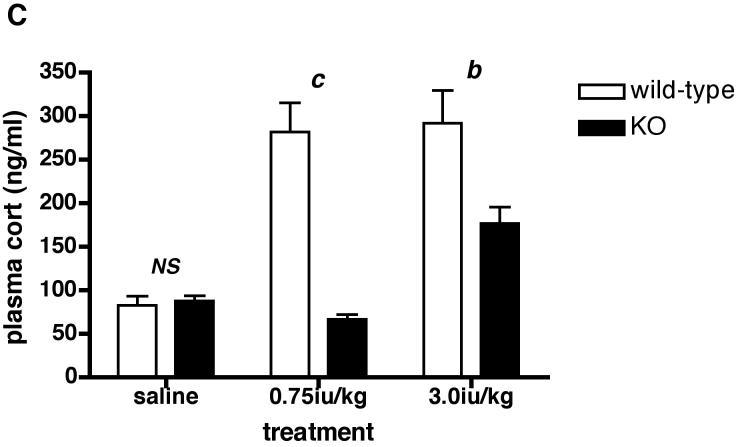
Figure 5.
Levels of plasma glucose (A), ACTH (B) and CORT (C) following peripheral (ip) administration of insulin (Actrapid) to Avpr1b-deficient mice.
Mice were sacrificed 1 h after treatment with saline vehicle, 0.75iu/kg or 3.0iu/kg insulin. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 3-4 mice/treatment. Plasma glucose = A: a, P < 0.05 0.75iu/kg insulin vs. 3.0iu/kg insulin. b, P < 0.01 saline vs. insulin-injected. b, P < 0.01 saline vs. insulin-injected. NS, no significant difference (P > 0.05) saline wild-type vs. saline KO; 0.75iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. 0.75iu/kg insulin KO; 3.0iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. 3.0iu/kg insulin KO. Plasma ACTH = B: a, P < 0.05 3.0iu/kg insulin KO vs. saline KO. b, P < 0.01 0.75iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. 0.75iu/kg insulin KO; 0.75iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. saline wild-type; 3.0iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. 0.75iu/kg insulin wild-type. c, P < 0.001 3.0iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. 3.0iu/kg insulin KO; 3.0iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. saline wild-type. NS, no significant difference (P > 0.05) saline wild-type vs. saline KO. Plasma CORT = C: b, P < 0.01 3.0iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. 3.0iu/kg insulin KO; 0.75iu/kg insulin KO vs. 3.0iu/kg insulin KO. c, P < 0.001 0.75iu/kg insulin wild-type vs. 0.75iu/kg insulin KO. NS, no significant difference (P >0.05) saline wild-type vs. saline KO.