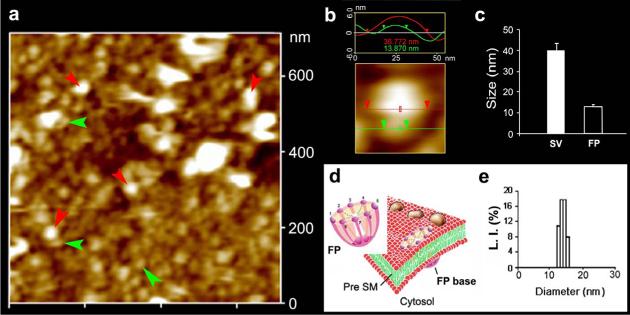
Figure 2. Neuronal fusion pore distribution, size and structure.
Figure 2a shows the structure and distribution of fusion pores at the cytosolic compartment of a synaptosome. Inside-out synaptosome preparations when imaged in buffer using AFM, demonstrates inverted 12−16 nm cup-shaped fusion pores, some with docked vesicles. Note one inverted cup-shaped fusion pore (green arrow heads), with a docked synaptic vesicle (red arrow heads), shown at higher magnification in Figure 2b. (b) Atomic force micrograph shows a 37 nm synaptic vesicle docked to a 14 nm fusion pore at the cytoplasmic compartment in the isolated synaptosomal membrane. (c) AFM measurement of the fusion pores (13.05±0.91) and attached synaptic vesicles (40.15±3.14) in the cytosolic compartment of synaptosome membrane, is demonstrated in Fig. 2c (n=15). (d) Schematic illustration of a neuronal fusion pore, showing the 8 vertical ridges and a central plug. (e) Photon correlation spectroscopy, further demonstrates fusion pores to measure 12−16 nm.