Figure 5. Two sequential measurements of fractional synthesis rate of Aß in the same participant.
The ratio of labeled Aß to unlabeled Aß over 36 hours is shown for a single participant who was intravenously given 13C6-leucine for 0 to 9 hours, followed by phenylalanine given from 16 to 25 hours of the study. Cerebral-spinal fluid was collected hourly during and after labeling for a total of 36 hours. Each hourly sample was immunoprecipitated for Aß, trypsin digested, and analyzed for percent leucine and phenylalanine labeled Aß. Note the rapid increase in leucine labeled Aß to plateau at 12 hours and a subsequent decline in labeled Aß after 24 hours. There is no detectable phenylalanine labeling until hour 20, followed by a rapid rise to plateau.
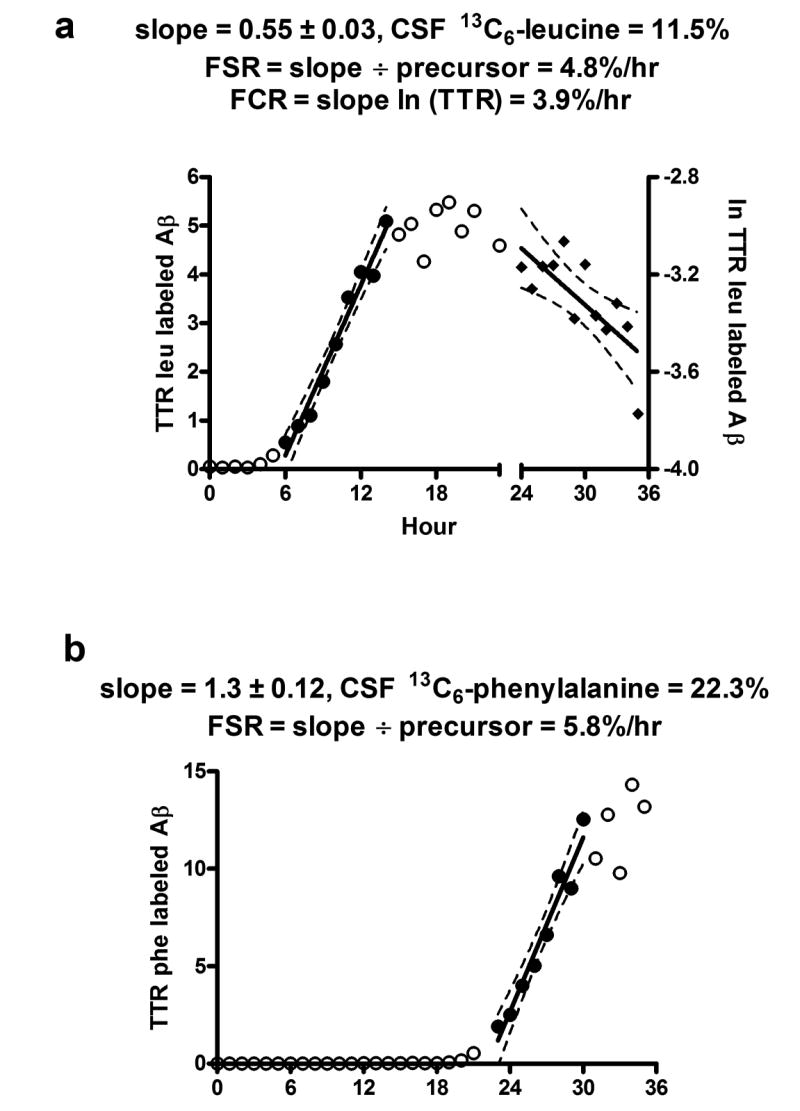
(a) Aβ17-28 labeled leucine tandem MS ions were quantified excluding 13C6-phenylalanine containing ions and plotted over 36 hours. Leucine labeled ions are detected 5 hours after onset of labeling. FSR was calculated using the slope of the linear regression shown divided by the 13C6-leucine enrichment in CSF.
(b)13C6-phenylalanine labeled Aβ17-28 tandem MS ions were quantified excluding 13C6-leucine containing ions and plotted over 36 hours from the same tandem MS data files as in (a). There are not detectable phenylalanine labeled ions during peak leucine labeled Aß times (5-20 hours). Phenylalanine labeled ions are detected 5 hours after onset of 13C6-phenylalanine labeling. FSR was calculated using the slope of the linear regression shown divided by the 13C6-phenylalanine enrichment in CSF.
