Fig. 2.
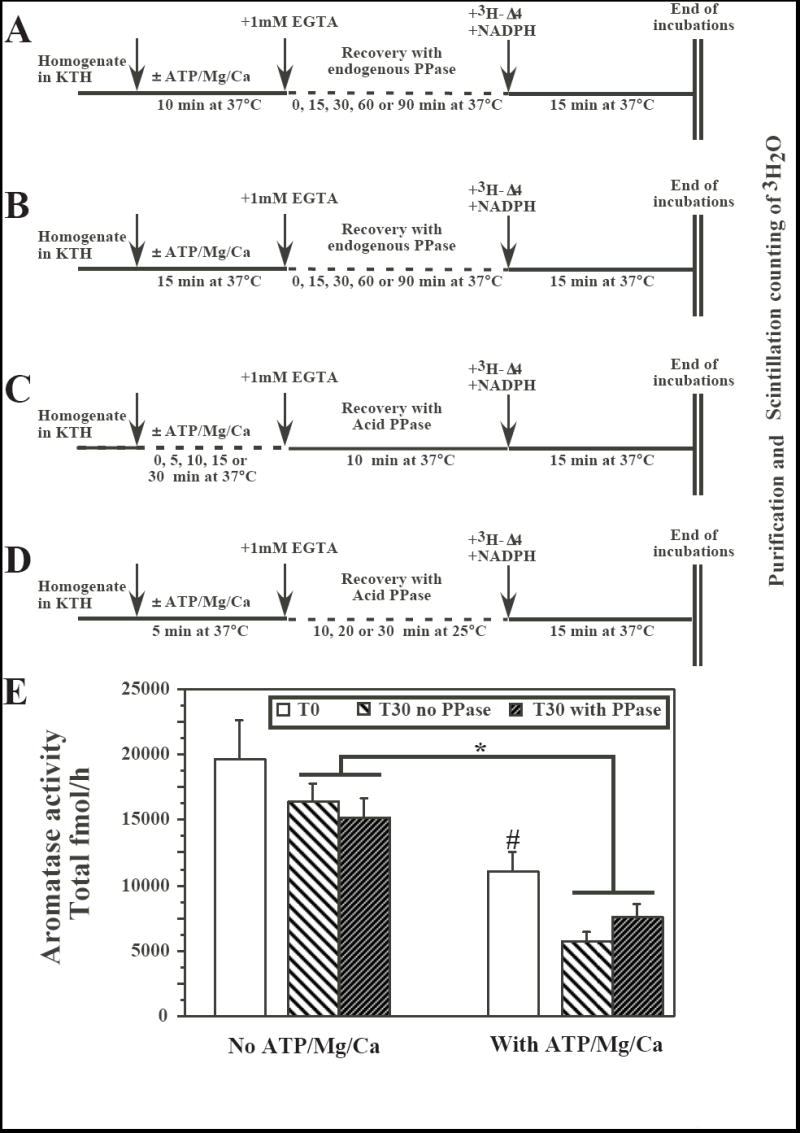
Effects of endogenous phosphatases or of exogenous acid (Ac) phosphatase (PPase; 0.4 units) on aromatase activity (AA) in preoptic-hypothalamic homogenates from male quail brain that had been previously exposed or not to phosphorylating conditions (presence of ATP/Mg/Ca). Panels A through D provide a schematic description of the different protocols that were tested. The sequential treatments that were applied to the homogenate aliquots are indicated by arrows and the duration of incubations and the temperatures at which they took place are listed below the horizontal line representing the time line (see also text for additional details). Panel E illustrates the results of a recovery experiment performed on three independent brain homogenates to further test the best conditions identified in the experiments schematized in A-D (Inhibition for 5 min with ATP/Mg/Ca, recovery in the presence of 0.4 unit Ac PPase for 30 min at 25°C). *= p<0.05 for the main effect in the ANOVA comparing at T30 samples exposed or not to ATP/Mg/Ca. This ANOVA identified no effect of the PPase and no interaction between the two factors. #= p<0.05 for the comparison of samples with or without ATP/Mg/Ca at T0.
