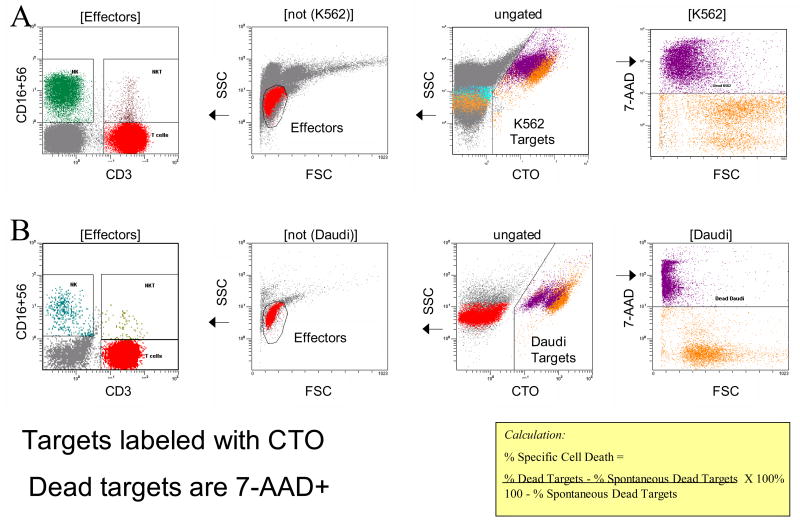
Figure 1.
Gating strategy used for the FCC assay. Identification of target cells: ungated events are shown in the third panel from the left. Target cells (K562) are identified as CTO+ events with high side scatter. The rightmost panel, gated on target cells only, shows forward scatter versus 7-AAD fluorescence. Dead K562 target cells (color-evented purple) in A or dead Daudi cells in B are identified by 7-AAD dye uptake and low forward scatter. Identification of effector cells: the second panel from the left is gated to exclude target cells and shows the light scatter characteristics of the peripheral blood mononuclear cells assayed for cytotoxicity. The leftmost panel, gated to include lymphoid light scatter events from the previous panel, and to exclude target cells, shows anti-CD3 ECD fluorescence, versus anti-CD16 plus CD56 FITC fluorescence. Effector cells are analyzed for expression of CD3, CD16 and CD56 to identify NK (CD3−CD16+CD56+), NKT (CD3+CD16+CD56+) and T cell (CD+CD16−CD56−) populations.