Fig. 5.
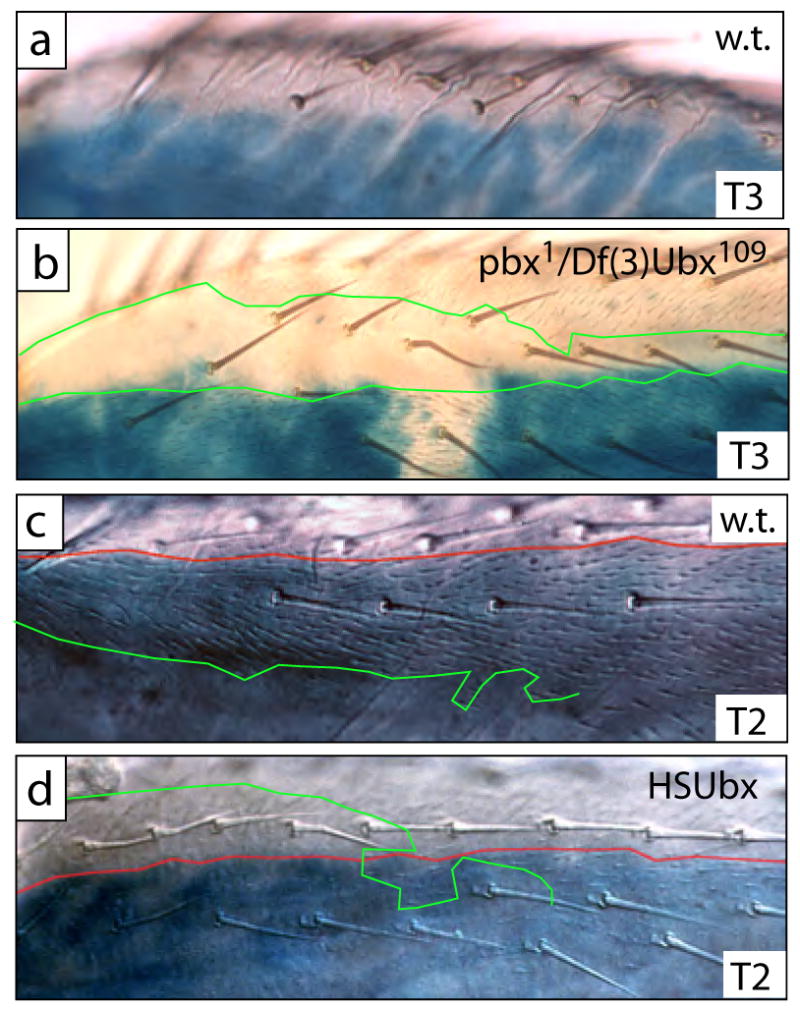
The boundary of naked cuticle and trichomes does not obey the compartment boundary in T2 or T3, and the proximal dorsal anterior femur of both T2 and T3 is competent to repress trichomes when high levels of Ubx are expressed in these cells. (a) In proximal dorsal regions of wild-type T3, naked cuticle is found in both posterior and anterior compartments. Blue en-lacZ staining marks the posterior compartment. (b) In a pbx1 hemizygote naked cuticle is still found in the anterior compartment, but cells in the posterior compartment differentiate trichomes. In this preparation, en-lacZ staining failed in a small patch of cells, revealing the faint trichomes. In most specimens this boundary of en-lacZ staining is complete and approximately straight, and the ectopic trichomes are only found within the region of en-lacZ staining. The boundaries of naked cuticle and trichomes are marked with green lines. (c) In dorsal proximal regions of wild-type T2 legs trichomes differentiate in both the anterior and posterior compartment. The boundary of en-lacZ staining is marked with a red line, and the boundary of trichomes is marked with a green line. (d) When Ubx is expressed ectopically at high levels at 24H APF, cells in this dorsal region now differentiate naked cuticle in both the posterior and anterior compartments. The boundary of en-lacZ staining is marked with a red line, and the border of naked cuticle is marked with a green line.
