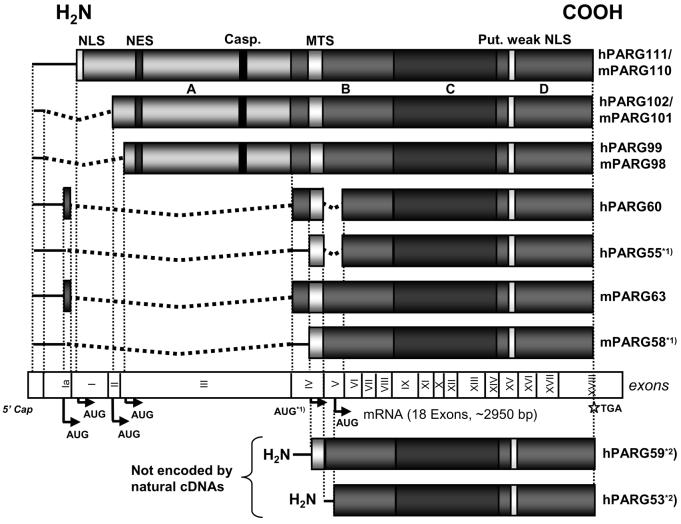
Fig. 5. PARG mRNA splice variants and resulting protein structures.
Open reading frames are represented by shaded boxes. Alternative splicing yields messages encoding 102 kDa and 99 kDa PARGs in human (100 kDa and 98 kDa in mouse) but also shorter PARG proteins of less than 65 kDa that were identified in both human and mouse RNA preparations. In hPARG60 and mPARG63 usage of a facultative exon (exon Ia) leads to alternative N-terminal protein sequences of 16 amino acids not found in the three long forms (i.e. 111 kDa, 102 kDa and 99 kDa) of the enzyme in both species. In human, exon V was consistently skipped in all cDNAs encoding hPARG60 isolated in this study but never in the other mRNAs encoding the three large protein variants. Skipping of exon V appears to be specific for human and was absent in murine cDNA preparations. Proteins hPARG55 and mPARG58 (indicated by *1)) are most likely not encoded by specific mRNAs but may be expressed from hPARG60 and mPARG63 messages, respectively, by alternative translation start codon usage as previously observed in the large PARG cDNAs [7]. *2) Human PARG59 and hPARG53 were not encoded by natural cDNAs obtained by RT-PCR but were constructed for the purpose of studying MTS function in this study.