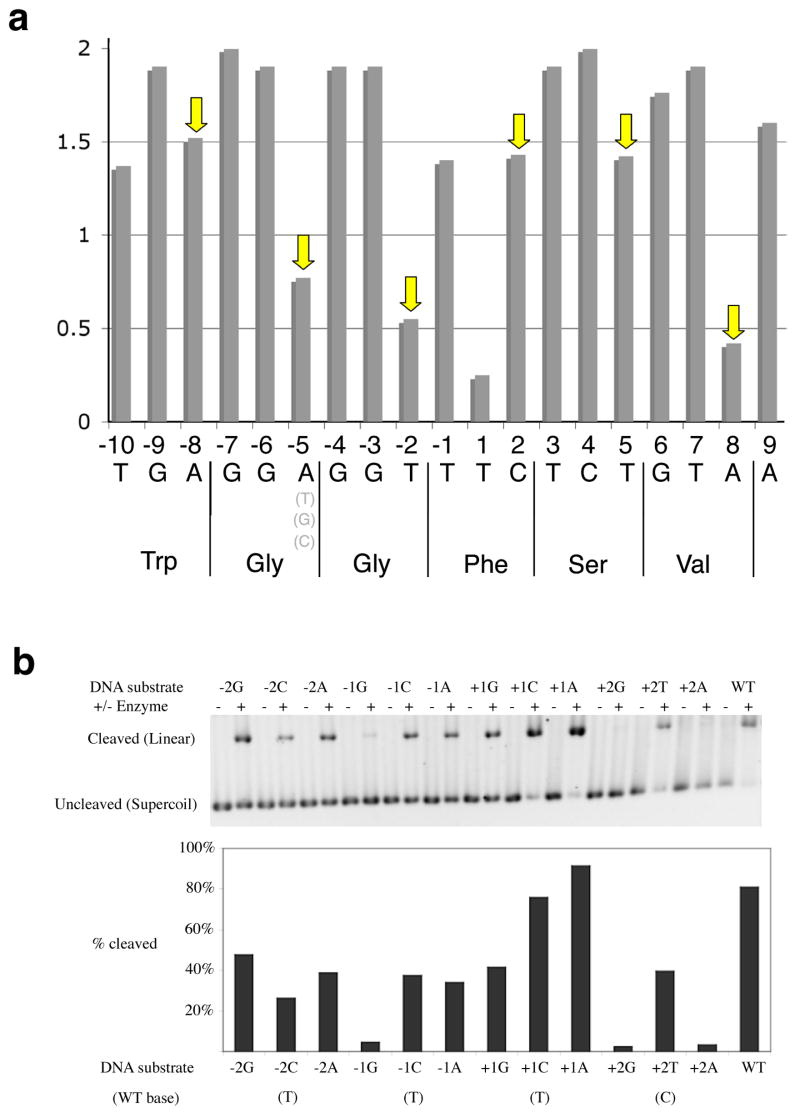
Figure 3. Specificity of DNA recognition by I-AniI.
Panel a. Information content at individual positions across the I-AniI target site, calculated using recovered sequences from a screen of site variants. The corresponding translated protein sequence of the host gene is provided below the DNA target sequence (note that in fungal mitochondrial genomes, ‘TGA’ encodes for Trp rather than ‘Stop’). The information content (specificity of recognition) was calculated at each basepair according to the method of Schneider, et al., 1986; “2” = invariant base preference). Arrows indicate wobble positions in host coding frame (average information content = 1.0, compared to 1.7 for non-wobble positions). Panel b. Cleavage of individual single base substitutions across the ‘central four’ positions in the target site. Three substitutions (−1G, +2G and +2A) are strongly disfavored; two (+1 G and A) are equivalent or superior to wild-type; the remainder are slightly reduced but within 2-fold of wild-type cleavage efficiency.