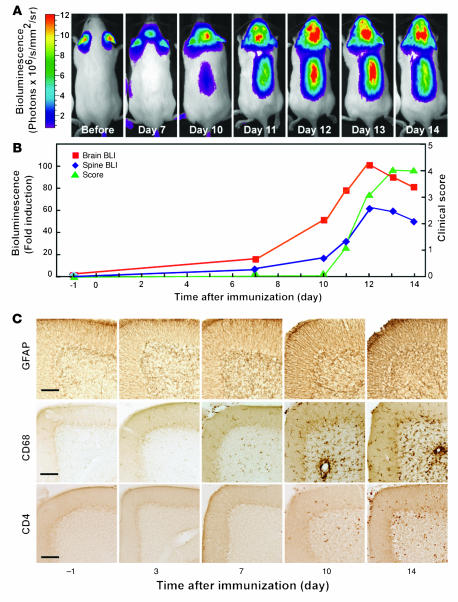
Figure 1. Astrogliosis and neuroinflammation precede clinical signs in EAE.
(A and B) EAE was induced in GFAP-luc mice with MOG35–55 emulsified in CFA plus PT, and bioluminescence was recorded in living mice (n = 7) injected with luciferin (150 mg/kg) 1 day before (–1) and at 3, 7, 10, or 14 dpi. Time course of bioluminescence recorded in a representative mouse (A) and the bioluminescence expressed as fold induction plotted with clinical score (B). (C) Mice were sacrificed at indicated time points. Sagittal brain sections from control (–1) or EAE mice sacrificed at different time points were examined for neuroinflammation, and images were taken from cerebellum. Neuroinflammation was assessed by immunohistochemistry as a function of astrogliosis (GFAP), microgliosis (CD68), and T lymphocyte infiltration (CD4). Scale bars: 100 μm.