Fig. 5.
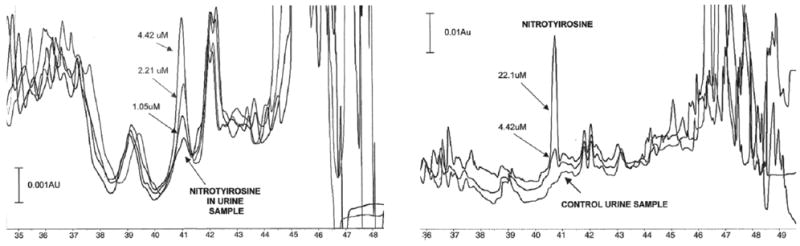
An example of HPCE/direct UV absorbance detection analysis of 3-nitrotyrosine in mammalian urine samples. Electrophoretic 3-nitrotyrosine peaks in urine samples from diabetic (left) and control (right) rats after large-volume sample stacking-CE. The samples were spiked with three or two levels of analyte 3-nitrotyrosine at 1.05, 2.21, 4.42 μM. BGE was 15 M phosphoric acid, 0.5 mM of CTAB at pH 6.4. Separations were performed in a 75-cm fused silica capillary, i.d. 50 μm, using −15 kV voltages. Pressure injection and direct UV detection (214 nm) was used. Reprinted from [292], Journal of Chromatography B 809, N. Maeso, A. Cifuentes, C. Barbas, Large-volume sample stacking-capillary electrophoresis used for the determination of 3-nitrotyrosine in rat urine, 147–152, 2004, with permission from Elsevier.
