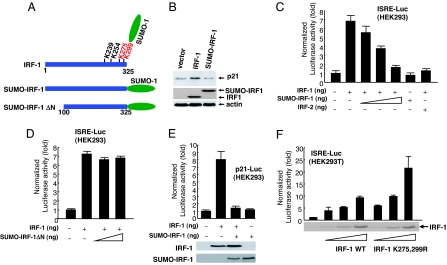
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of IRF-1-dependent transcription by SUMOylated IRF-1. (A) Schematic diagram of SUMO-IRF-1 and SUMO-IRF-1 ΔN. K275 and the major SUMOylation site of IRF-1 at K299. (B) SUMO-IRF-1 does not induce p21 transcription. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with IRF-1 and SUMO-IRF1. (C) Transcription of ISRE fused to a Luc gene (ISRE-Luc) was inhibited by SUMO-IRF-1 in the presence of IRF-1 in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with 300 ng of ISRE-Luc, 300 ng of an IRF-1 expression plasmid (pcDNA3/IRF-1), and increasing concentrations of plasmid-encoding SUMO-IRF-1 (pcDNA3/SUMO-IRF-1) (10, 100, and 300 ng). IRF-2 was used as a positive control. (D) SUMO-IRF-1 ΔN does not repress transcriptional activation by IRF-1. (E) The human p21 promoter was inhibited by SUMO-IRF-1 in the presence of IRF-1. (F) The SUMOylation-deficient mutant (K275,299R) of IRF-1 increased transcriptional activity. HEK293T cells were transfected with 200 ng of ISRE-Luc and increasing concentrations of plasmid encoding IRF-1 or IRF-1 mutant (5, 10, and 25 ng) (Upper). Cell lysates were probed with anti-IRF-1 antibodies (Lower) to verify the level of IRF-1 proteins.