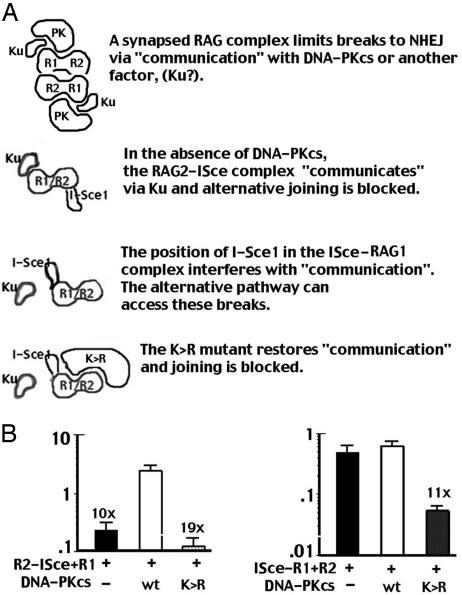
Fig. 5.
Does DNA-PK interact with the RAG complex to direct breaks into the NHEJ pathway? (A) The RAG complex interacts with both Ku and DNA-PKcs. With the RAG2–I-Sce1 fusion protein, I-Sce1 does not interfere with either interaction. Breaks are restricted to NHEJ in both xrs6 and V3 cells. In contrast, the position of I-Sce1 in the I-Sce1–RAG1 fusion protein interferes with the Ku interaction. Without DNA-PKcs, the alternative pathway efficiently joins breaks. In the presence of DNA-PKcs, breaks are NHEJ restricted, but also are efficiently joined because NHEJ is intact. However, in the presence of NHEJ-defective DNA-PKcs, breaks are restricted to NHEJ, but joining is blocked because NHEJ is defective. (B) (Left) Transient recombination assays were performed in V3 cells, including the I-Sce1 substrate p28-7, RAG2–I-Sce1/RAG1, and no DNA-PKcs, wild-type DNA-PKcs, or K>R mutant as indicated. (Right) Transient recombination assays were performed in V3 cells, including the I-Sce1 substrate p28-7, I-Sce1–RAG1/RAG2, and no DNA-PKcs, wild-type DNA-PKcs, or K>R mutant as indicated. The results show the average and average deviation of three independent experiments.