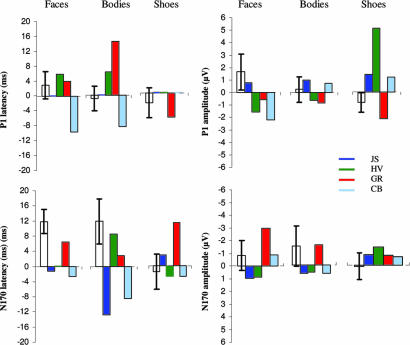
Fig. 2.
Inversion effects for P1 and N170 component on right hemisphere electrodes. P1 and N170 latencies (ms) and amplitudes (μV) were pooled over right-hemisphere electrodes for prosopagnosic individuals against the control group (confidence interval 95%). Normal inversion occurs when amplitudes/latencies are greater for inverted than upright stimuli (i.e., above the dotted axis). Paradoxical inversion occurs when amplitudes/latencies are smaller for inverted than upright stimuli (i.e, underneath the dotted axis).