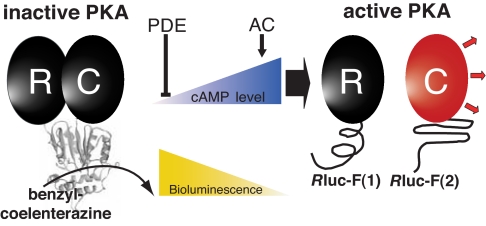
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the PCA strategy using Rluc fragments to study the dynamic complex of the PKA heterodimer [regulatory (R) and catalytic (C) PKA subunits] in vivo. Cellular cAMP levels are controlled directly by adenylyl cyclases (AC, production) and PDE (degradation). cAMP elevation and association with the R subunit of PKA induces dissociation of R and C subunits, resulting in decreasing Rluc-PCA activity.