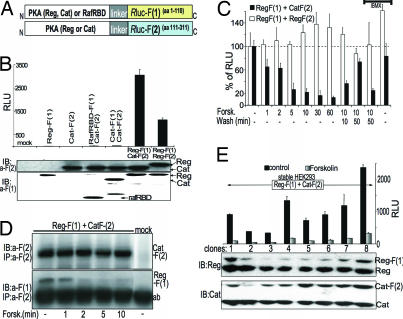
Fig. 2.
A dynamic PKA activity sensor based on Rluc-PCA. (A) Schematic representation for the design of a PCA-based PKA reporter. The regulatory (Reg) and catalytic (Cat) PKA subunits were fused to fragment 1 [F(1)] or fragment 2 [F(2)] of Rluc. (B) The Rluc-PCA was detected from transiently transfected HEK293T cells in suspension aliquoted to 96-well microtiter plates. Immunoblot analysis verifies expression of PCA-tagged proteins (representative experiment ± SD of triplicates). RLU, relative luminescence units. (C) Effect of forskolin (100 μM) and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (100 μM) treatment on Reg-F(1):Cat-F(2) and Reg-F(1):Reg-F(2). The Rluc-PCA was detected from transiently transfected HEK293T cells in suspension and aliquoted to 96-well microtiter plates (mean ± SD from three independent experiments). (D) HEK293T cells coexpressing Reg-F(1):Cat-F(2) were treated for the indicated times with forskolin (100 μM) and were subjected to immunoprecipitation and Western blotting using anti-Rluc antibodies. (E) The Rluc-PCA was detected from untreated and forskolin-treated (100 μM, 15 min) HEK293T cells stably expressing Reg-F(1):Cat-F(2) in suspension (± SD from three independent samples). Immunoblot analysis shows the expression of endogenously expressed and overexpressed PKA subunits.