Abstract
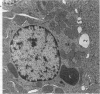
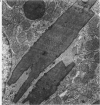
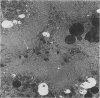
The distribution of copper and related changes have been studied in copper-loaded rat kidneys at the ultrastructural level by X-ray electron probe microanalysis, in order to clarify the pathogenesis of copper-induced damage and subsequent recovery in this organ. Male rats fed a high copper diet (1500 ppm) for 16 weeks were killed at intervals; their kidneys were removed and portions of kidney cortex fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and 2% glutaraldehyde for electron microscopy: other samples were analysed for copper by AA spectrophotometry. Increasing copper accumulation was associated with progressive PCT cell disarray and characterized by irreversible nuclear damage coincident with the intranuclear accumulation of Cu, S, P, and Ca. Copper was also identified within structurally intact lysosomes associated with Zn and Fe (Type I lysosomes) or P and S (Type II lysosomes, putative Cu-MT). Subsequent copper decline and tubular recovery was associated with the facilitated lysosomal sequestration of copper and excretion of copper-containing cell products into the tubule lumina, Cu-MT and alpha-2 urinary protein-copper. The cytotoxicity of copper in the kidney, as well as the liver, is associated primarily with irreversible nuclear damage, whereas lysosomal copper sequestration protects the cell from injury.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan S. E., Frieden E. Interaction of copper(II) with deoxyribonucleic acid below 30 degrees. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2728–2734. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERICSSON J. L. TRANSPORT AND DIGESTION OF HEMOGLOBIN IN THE PROXIMAL TUBULE. I. LIGHT MICROSCOPY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF ACID PHOSPHATASE. Lab Invest. 1965 Jan;14:1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuentealba I. C., Haywood S., Trafford J. Evaluation of histochemical methods for the detection of copper overload in rat liver. Liver. 1987 Oct;7(5):277–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1987.tb00356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuentealba I., Haywood S. Cellular mechanisms of toxicity and tolerance in the copper-loaded rat. I. Ultrastructural changes in the liver. Liver. 1988 Dec;8(6):372–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1988.tb01019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuentealba I., Haywood S., Foster J. Cellular mechanisms of toxicity and tolerance in the copper-loaded rat. II. Pathogenesis of copper toxicity in the liver. Exp Mol Pathol. 1989 Feb;50(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(89)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooneratne S. R., Howell J. M., Aughey E. An ultrastructural study of the kidney of normal, copper poisoned and thiomolybdate-treated sheep. J Comp Pathol. 1986 Nov;96(6):593–612. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(86)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooneratne S. R., Howell J. M., Cook R. D. An ultrastructural and morphometric study of the liver of normal and copper-poisoned sheep. Am J Pathol. 1980 May;99(2):429–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooneratne S. R., Howell J. M., Gawthorne J. Intracellular distribution of copper in the liver of normal and copper loaded sheep. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jul;27(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. J., Bryan S. E. Localization and uptake of copper into chromatin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 Jul;33(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood S. Copper toxicosis and tolerance in the rat. I--Changes in copper content of the liver and kidney. J Pathol. 1985 Feb;145(2):149–158. doi: 10.1002/path.1711450203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood S., Loughran M., Batt R. M. Copper toxicosis and tolerance in the rat. III. Intracellular localization of copper in the liver and kidney. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985 Oct;43(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(85)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood S. The effect of excess dietary copper on the liver and kidney of the male rat. J Comp Pathol. 1980 Apr;90(2):217–232. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(80)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssens A. R., Van Noord M. J., Van Hoek C. J., Ruiter D. J., Mauw B. J., Van den Hamer C. J. The lysosomal copper concentration in the liver in primary biliary cirrhosis. Liver. 1984 Dec;4(6):396–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1984.tb00956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. B., Gooneratne S. R., Howell J. M. X-ray microanalysis of liver and kidney in copper loaded sheep with and without thiomolybdate administration. Res Vet Sci. 1984 Nov;37(3):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa K., Nakanishi I., Kuroda K. Morphological changes of the kidney and bone of rats in chronic cadmium poisoning. Exp Mol Pathol. 1981 Feb;34(1):9–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(81)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER H. Copper excretion in the urine of normal individuals and of patients with hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson's disease). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Apr;31(2):262–265. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deVries C. R., Ingram P., Walker S. R., Linton R. W., Gutknecht W. F., Shelburne J. D. Acute toxicity of lead particulates on pulmonary alveolar macrophages. Ultrastructural and microanalytical studies. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]