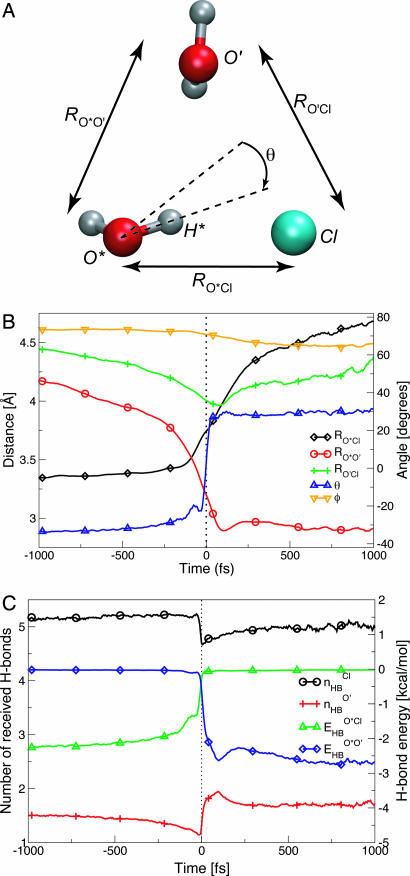
Fig. 1.
Time evolution, centered on the H-bond switching event, of the geometric parameters defined in A and presented in B, together with C, which represents the change in the number of H-bonds received by the different partners in A. (A) Geometric coordinate definitions: RO*Cl and RO*O′ are the oxygen–chloride and oxygen–oxygen distances between the rotating water and its initial and final partners, and RO′Cl is the distance between initial and final partners; θ is the angle between the rotating O*H* bond and the bisector plane of the ClO*O′ angle φ. (B) Time evolution of these geometric quantities, averaged over 4,279 switch events. (C) nHBCl and nHBO′ are the number of H-bonds accepted, respectively, by Cl− and O′ (see Methods); E HBO*Cl and E HBO*O′ are the O*H*···Cl− and O*H*···O′ H-bond energies (see Methods).