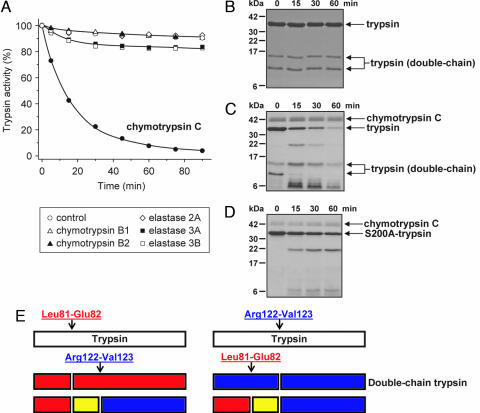
Fig. 1.
Degradation of human cationic trypsin by chymotrypsin C. (A) Cationic trypsin (2 μM) was incubated alone (control) or with 300 nM of the indicated proteases in 0.1 M Tris·HCl (pH 8.0) and 25 μM CaCl2 (final concentrations) in 100 μl of final volume. At the indicated times, 2-μl aliquots were withdrawn, and residual trypsin activity was measured and expressed as a percentage of the initial activity. (B–D) SDS/PAGE analysis of autolysis and chymotrypsin C-mediated degradation of cationic trypsin. Wild-type cationic trypsin (B and C) or S200A mutant cationic trypsin (D) were incubated at 2 μM concentration in the absence (B) or presence (C and D) of 300 nM chymotrypsin C in 0.1 M Tris·HCl (pH 8.0) and 25 μM CaCl2 (final concentrations). At the indicated times, 100-μl aliquots were precipitated with 10% trichloroacetic acid (final concentration) and electrophoresed on 15% minigels under reducing conditions, followed by Coomassie blue staining. Note that chymotrypsin C is glycosylated and runs as a fuzzy band. Double-chain trypsin is cleaved at the Arg122-Val123 peptide bond and runs as two bands on reducing gels; the upper band corresponds to the C-terminal chain (Val123-Ser247), and the lower band is the N-terminal chain (Ile24-Arg122). (E) Major proteolytic cleavage sites in cationic trypsin determined from N-terminal sequencing of the visible bands in C.