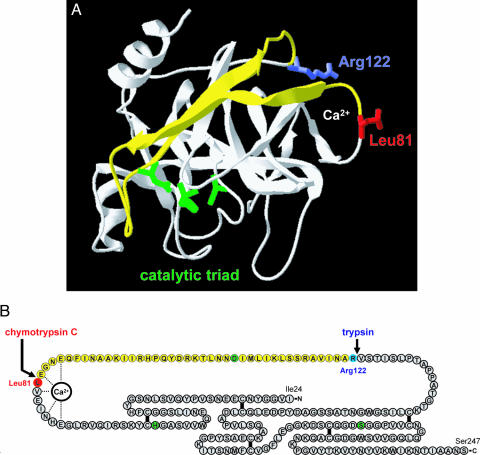
Fig. 2.
Structural determinants of chymotrypsin C-mediated trypsin degradation. (A) Ribbon diagram of human cationic trypsin [Protein Data Bank ID code 1TRN; chain B of the crystallographic dimer shown here (21)] with the Leu81 (red) and Arg122 (blue) side chains indicated. The calcium-binding loop is denoted by the Ca2+ symbol. The catalytic triad consisting of His63 (His57 in the conventional chymotrypsin numbering); Asp107 (chymotrypsin no. Asp102) and Ser200 (chymotrypsin no. Ser195) are shown in green. Note that Asp107 is located on the yellow peptide segment, which is released upon cleavage of the Leu81-Glu82 and Arg122-Val123 peptide bonds. See text for details. The image was rendered using DeepView/Swiss-PdbViewer version 3.7. (B) Primary structure of human cationic trypsin. Individual amino acids are represented by circles. The catalytic triad is highlighted in green, Leu81 is in red, and Arg122 is in blue. The five disulfide bridges and the interactions between the calcium ion and amino acids within the calcium binding loop are indicated. Note that both the Leu81-Glu82 and the Arg122-Val123 peptide bonds are located in a long peptide segment not stabilized by disulfide bonds. The yellow section corresponds to the yellow peptide in A.