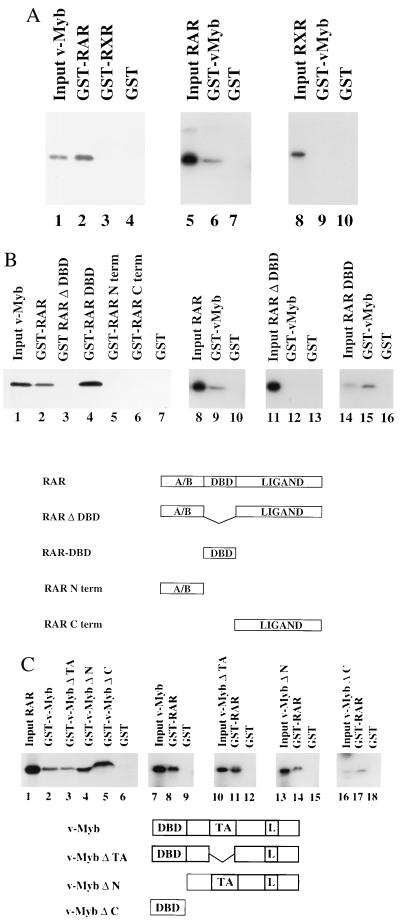
Figure 4.
v-Myb and RAR physically interact in vitro. (A) v-Myb physically interacts with RAR but not with RXR. The ability of RAR and RXR proteins to interact with v-Myb was evaluated by GST-pulldown assays. RAR and RXR were expressed as GST-fusion proteins, immobilized to glutathione-linked Sepharose beads and tested for interaction with in vitro-translated, [35S]methionine-labeled v-Myb. In the reciprocal experiment GST-v-Myb was tested with in vitro-translated, [35S]methionine-labeled RAR and RXR. The same amounts of either GST or GST fusion proteins were linked to glutathione Sepharose beads. The input control in lanes 1, 5, and 8 reflects 10% of the total amount of [35S]methionine-labeled proteins used for the pulldown experiments. (B) The DBD of RAR is necessary and sufficient for interaction with v-Myb. To localize the domain within RAR necessary for interaction with v-Myb either full-length RAR or various mutants thereof were expressed as GST-fusion proteins and tested for interaction with in vitro-translated, [35S]methionine-labeled v-Myb. In the reciprocal set of experiments GST-v-Myb was tested with in vitro-translated, [35S]methionine-labeled RAR or mutants thereof. The input control reflects 10% of the total amount of [35S]methionine-labeled proteins used for the pulldown assay. The full-length hRAR protein is composed of the N-terminal (A/B) domain, the DBD, and the C-terminal ligand binding domain (Ligand). (C) Several domains of v-Myb are involved in interaction with RAR. v-Myb and various mutants of v-Myb were either expressed as GST-fusion proteins or in vitro translated in the presence of [35S]methionine and tested in GST-pulldown experiments. v-Myb and v-Myb mutant proteins are illustrated schematically. L, leucine zipper.