Abstract
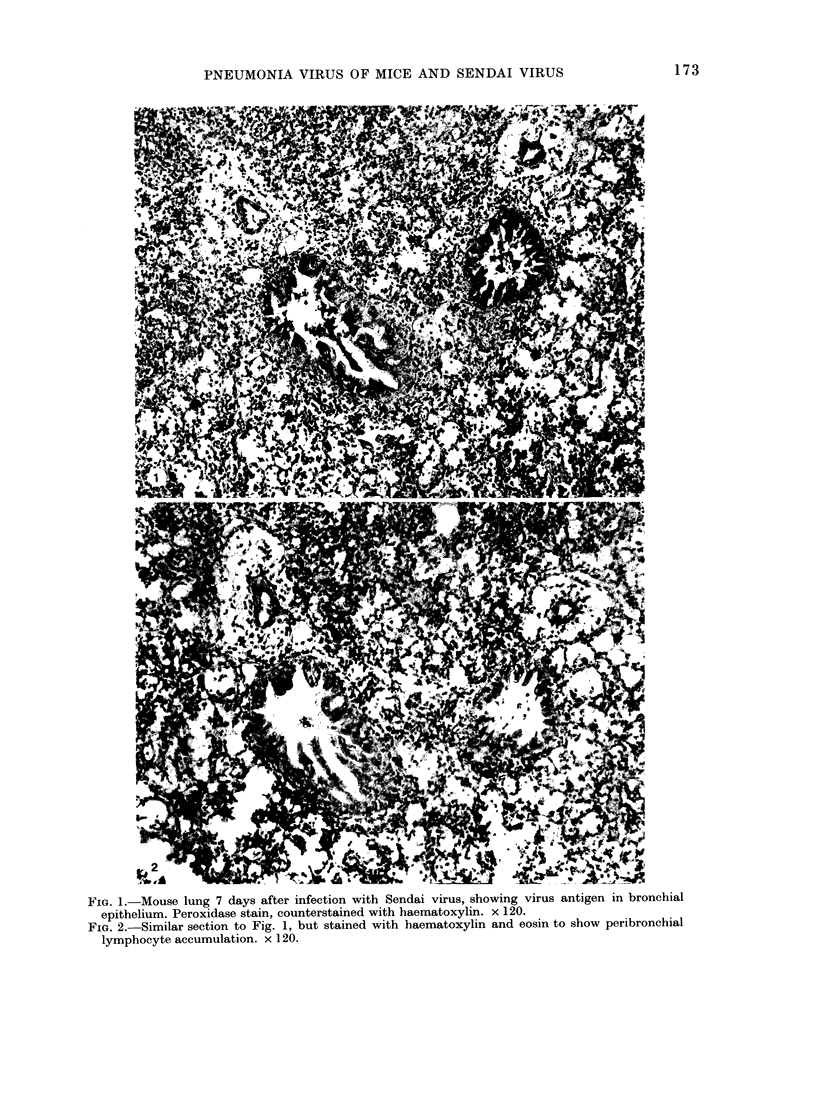
The pathogenicity and persistence of pneumonia virus of mice (PVM) and Sendai virus has been studied using germ-free nu/nu mice. PVM was found to infect cells of the bronchial epithelium (and the alveolar wall) of the lungs of germ-free nu/nu mice using the immunoperoxidase technique. The virus was located in the bronchial epithelium for 11 days before elimination, but persisted in the alveolar wall for the duration of the experiment (20 days). After Day 10 a humoral antibody response to PVM was observed which persisted, although at a low level (1 in 40), by haemagglutination-inhibition (HI) testing. Sendai virus in nu/nu mice also infected cells of the bronchial epithelium and this persisted for the duration of the experiment (27 days). The persistence of virus in the bronchial epithelium in relation to lack of humoral antibody is discussed with reference to local secretory antibody production, especially since this does not occur with PVM.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mims C. A., Murphy F. A. Parainfluenza virus Sendai infection in macrophages, ependyma, choroid plexus, vascular endothelium and respiratory tract of mice. Am J Pathol. 1973 Mar;70(3):315–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. W., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. The pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection in the mouse lung. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):89–95. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TENNANT R. W., PARKER J. C., WARD T. G. VIRUS STUDIES WITH GERMFREE MICE. II. COMPARATIVE RESPONSES OF GERMFREE MICE TO VIRUS INFECTION. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Mar;34:381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]