Abstract
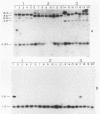
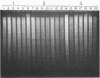
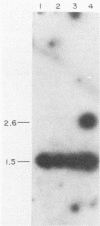
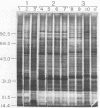
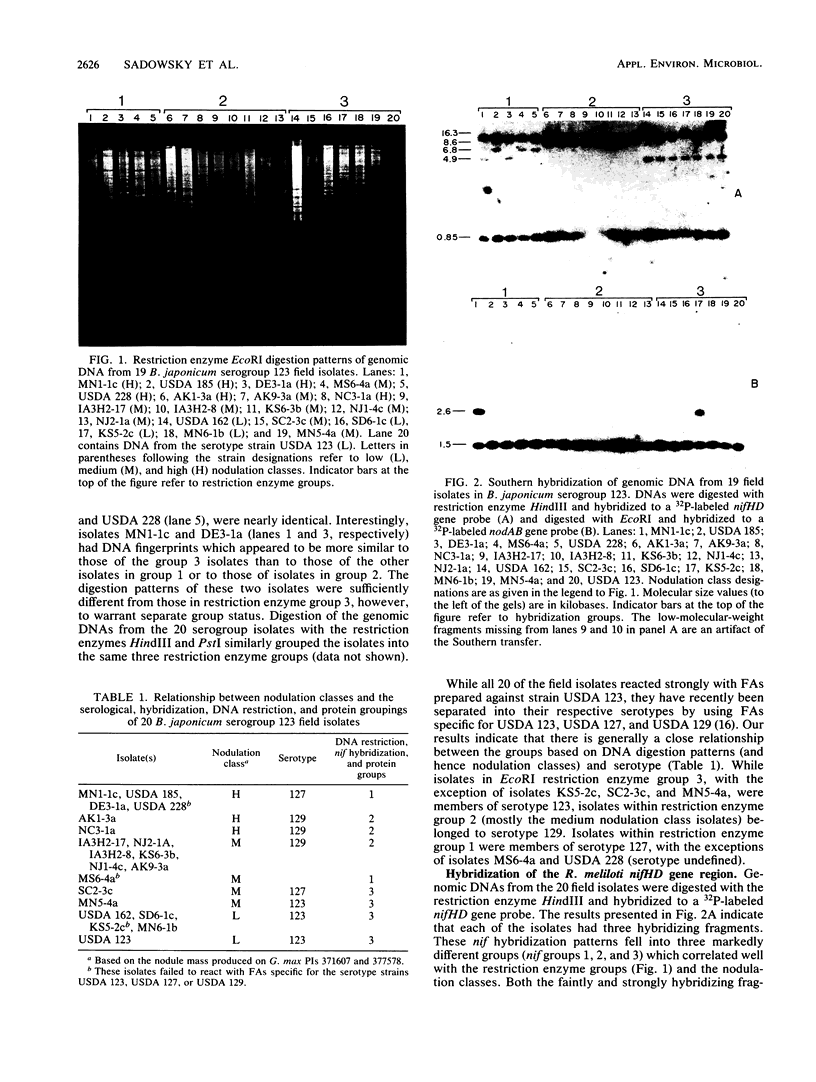
The genetic diversity among 20 field isolates of Bradyrhizobium japonicum serogroup 123 was examined by using restriction endonuclease digestions, one-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of total cell proteins, Southern hybridization analysis of nif and nod genes, and intrinsic antibiotic resistance profiles. All of the isolates were previously separated into three broad nodulation classes (low, medium, and high) based on their ability to form symbioses with specific soybean genotypes. Results of our studies indicate that there is a relationship between these three genotype-specific nodulation classes and groupings that have been made based on genomic DNA digestion patterns, sodium dodecyl sulfate-protein profiles, and Southern hybridizations to a nifHD gene probe. Intrinsic antibiotic resistance profiles and nodAB gene hybridizations were not useful in determining interrelationships between isolates and nodulation classes. Southern hybridizations revealed that two of the isolates had reiterated nod genes; however, there was no correlation between the presence of extra nodAB genes and the nodulation classes or symbiotic performance on permissive soybean genotypes. Hybridizations with the nif gene probe indicated that there is a relationship among serogroup, nodulation class, and the physical organization of the genome.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole M. A., Elkan G. H. Transmissible resistance to penicillin G, neomycin, and chloramphenicol in Rhizobium japonicum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DATE R. A., DECKER A. M. MINIMAL ANTIGENIC CONSTITUTION OF 28 STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Feb;11:1–8. doi: 10.1139/m65-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudman W. F. Antigenic analysis of Rhizobium japonicum by immunodiffusion. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jun;21(6):973–985. doi: 10.1128/am.21.6.973-985.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley R. G., Eaglesham A. R., Szalay A. A. Conservation of DNA regions adjacent to nifKDH homologous sequences in diverse slow-growing Rhizobium strains. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):225–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber T. A., Agarwal A. K., Keister D. L. Extracellular polysaccharide composition, ex planta nitrogenase activity, and DNA homology in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1168–1171. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1168-1171.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Cregan P. B. Nodulation and Competition for Nodulation of Selected Soybean Genotypes among Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serogroup 123 Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2631–2635. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2631-2635.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Weber D. F., Uratsu S. L. Rhizobium japonicum Serogroup and Hydrogenase Phenotype Distribution in 12 States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):613–615. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.613-615.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., van Berkum P., Weber D. F. A Comparative Study of the Physiology of Symbioses Formed by Rhizobium japonicum with Glycine max, Vigna unguiculata, and Macroptilium atropurpurem. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1626–1630. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEANS U. M., JOHNSON H. W., DATE R. A. QUICK SEROLOGICAL METHOD OF CLASSIFYING STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM IN NODULES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:547–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.547-553.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. C., Pueppke S. G. Differentiation of Rhizobium japonicum strain derivatives by antibiotic sensitivity patterns, lectin binding, and utilization of biochemicals. Can J Microbiol. 1980 May;26(5):606–612. doi: 10.1139/m80-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moawad H. A., Ellis W. R., Schmidt E. L. Rhizosphere Response as a Factor in Competition Among Three Serogroups of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum for Nodulation of Field-Grown Soybeans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):607–612. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.607-612.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Brill W. J. Diversity and Dynamics of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum Populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):931–938. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.931-938.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Schell M. G., Nelson K. K., Halverson L. J., Sirotkin K. M., Stacey G. Isolation and characterization of the DNA region encoding nodulation functions in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1301-1308.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Zidwick M. J., Abebe H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serocluster 123 and Diversity among Member Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1212-1215.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrdleta V. Serological analysis of eleven strains of Rhizobium japonicum. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(1):77–83. doi: 10.1007/BF02219118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Brown G. G., Verma D. P. Slow-growing Rhizobium japonicum comprises two highly divergent symbiotic types. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.148-154.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B. Estimation of DNA sequence divergence from comparison of restriction endonuclease digests. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1257–1265. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]