Figure 4.
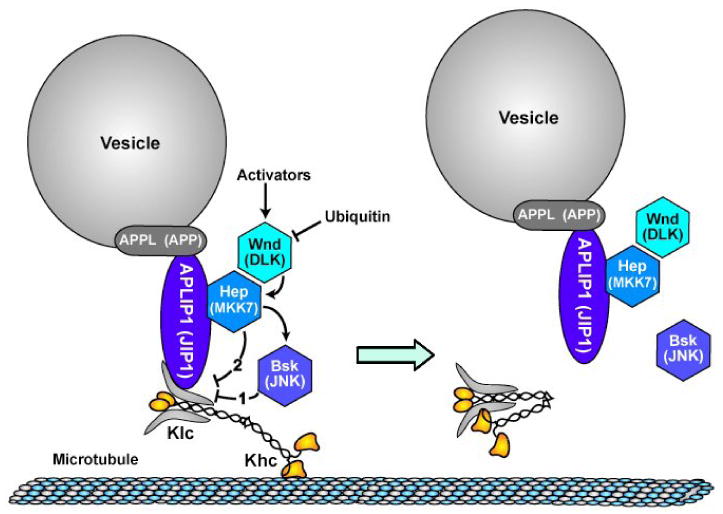
A model for Wnd (MAPKKK) pathway control of APLIP1 (JIP1)-linked kinesin-1 cargo transport. Components are labeled with Drosophila names and parenthetically with names of vertebrate homologs. Lines with arrowheads indicate activation influences and lines with crossbars indicate inhibition influences. Wnd (MAPKKK), whose levels can be modulated by ubiquitination, is activated by unknown upstream signals. Wnd activates Hep (MAPKK) by phosphorylation and activated Hep (MAPKK) then causes dissociation of APLIP1 (JIP1) from Klc, probably by phospho-activation of Bsk (JNK), which then directly or indirectly modifies the linkage complex (pathway 1). It is also possible that phosphorylation of Hep (MAPKK) causes a conformational change in the linkage complex that inhibits APLIP1 (JIP1)-Klc binding independent of Bsk (pathway 2). Disruption of the APLIP1 (JIP1)-Klc linkage may allow kinesin to adopt an inactive, folded conformation that does not bind to microtubules [29, 30].
