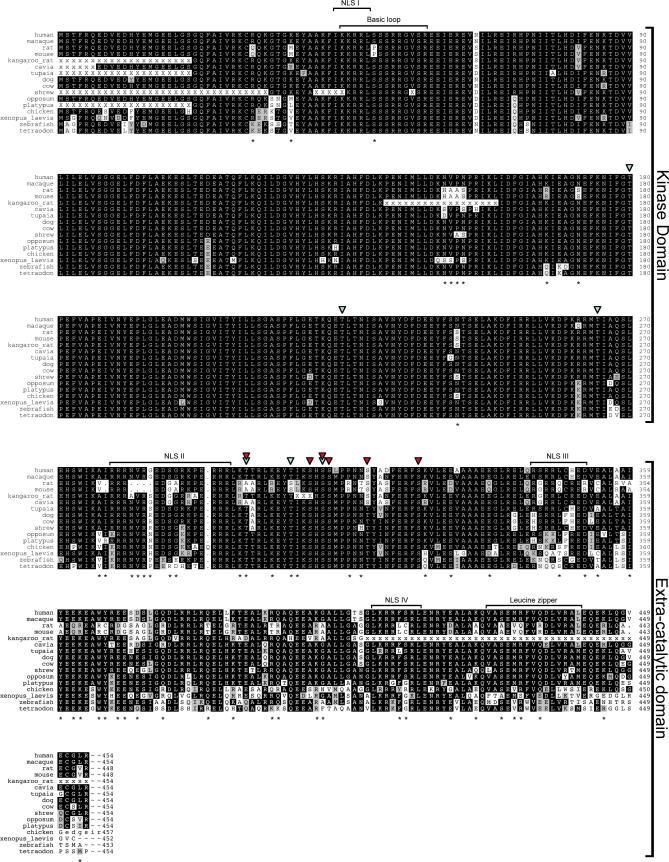
Figure 1. Multiple Sequence Alignment of the ZIPK Protein.
ZIPK protein sequences of the indicated organisms were extracted from the nonredundant database and from organism-specific genome projects, and aligned using the DIALIGN2 program. The alignment was corrected to allow the arginine triplet at position 278–280 of the rodent sequences to align with similar triplets in the other sequences. X's indicate unknown residues in partial sequences. Black shading indicates identity, grey shading indicates similarity. Asterisks mark sites of divergence of the rat and mouse orthologs from the mammalian consensus. Blue arrowheads indicate sites of autophosphorylation [5]; red arrowheads indicate sites of DAPK phosphorylation [8]. Putative NLSs I, II, and III, functional NLS IV, the basic loop, and the leucine zipper are indicated. Sequences of 16 representative organisms are displayed, representing fish, amphibians, birds, mammals, and, in particular, rodents. The full multiple sequence alignment of all ZIPK sequences used in this work is in Figures S1–S3.