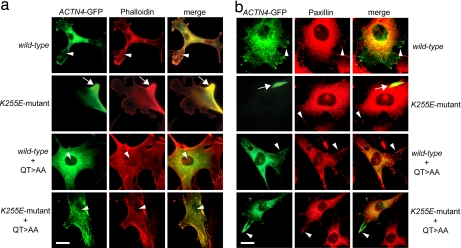
Fig. 5.
Actn4-deficient fibroblasts expressing WT or K255E mutant ACTN4–GFP containing the QT>AA mutation exhibit normal distribution of α-actinin-4–GFP. (a) Actn4-deficient fibroblasts were transfected with WT or K255E mutant ACTN4–GFP (green) without and with the QT>AA mutation and were stained with rhodamine–phalloidin (red). Images were merged; areas of colocalization appear yellow. Arrowheads point to normal distribution of α-actinin-4–GFP along actin stress fibers in cells expressing WT, WT+QT>AA, and K255E mutant+QT>AA ACTN4 constructs. In contrast, K255E mutant-expressing cells show α-actinin-4 staining associated exclusively with a large peripheral aggregate that also exhibits strong phalloidin staining, whereas F-actin stress fibers are absent. (b) Actn4-deficient fibroblasts were transfected with the various ACTN4–GFP constructs (green) and coimmunostained with an antibody against paxillin, a focal adhesion marker (red). All transfected cells exhibit paxillin staining at focal adhesion sites (arrowheads). Cells expressing WT, WT+QT>AA, or K255E mutant+QT>AA ACTN4–GFP showed normal peripheral expression of α-actinin-4 at focal adhesions that colocalized with paxillin staining. In contrast, K255E mutant-expressing cells show α-actinin-4 staining exclusively in a large aggregate (arrows), and α-actinin-4–GFP is absent from focal adhesions in these cells. (Scale bars, 25 μm.)