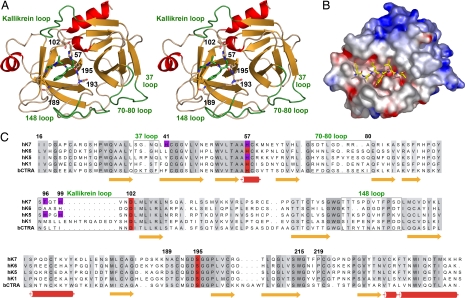
Fig. 2.
Tertiary and primary structure of hK7. (A) Overall structure of hK7E monomer with the AAF-CMK inhibitor in a stereo ribbon representation. Side chains of the catalytic triad (His57, Asp102, Ser195), the specificity-determining Asn189 in the S1 pocket, the oxyanion hole forming Gly193, and the double covalently bound inhibitor are depicted as stick models. Important loops are labeled and highlighted in green. (B) Electrostatic surface representation for hK7I in a hypothetical complex with the modeled peptide Glu-Ala-Leu-Tyr-Leu-Val, occupying the specificity sites S4 to S2′. (C) Sequence alignment of hK7 with the tissue kallikreins hK6, hK1, hK5, and bovine chymotrypsin as a reference for numbering. Residues involved in metal binding are indicated by magenta background, whereas loops are surrounded by boxes.