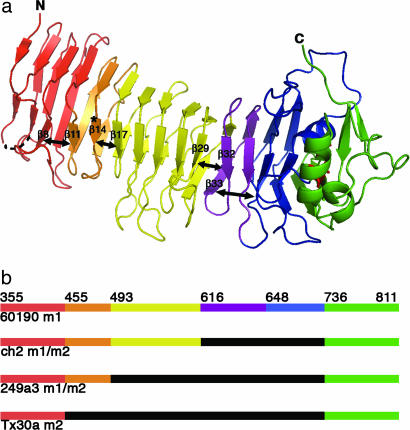
Fig. 2.
The VacA p55 structure reveals marked disruptions in β-sheet contacts. (a) Breaks in the β-sheet contacts (depicted with double-headed arrows) result in subdomains (SD) within the β-helix: SD-1 (red, 355–454), SD-2 (orange, 455–492), SD-3 (yellow, 493–615), SD-4 (purple, 616–647), and SD-5 (blue, 648–735). The C-terminal domain and disulfide bond are colored green and red, respectively, and the site of the m2 23-aa insertion is indicated by an asterisk. (b) This schematic shows prototype m1 and m2 VacA proteins (strains 60190 and Tx30a, respectively) and two naturally occurring m1m2 chimeras. The breaks in β-sheet contacts (a) correlate with sites of homologous recombination (see also SI Fig. 7). In this schematic the midregion that distinguishes type m1 and type m2 sequences is colored orange/yellow/purple/blue (m1) or black (m2).