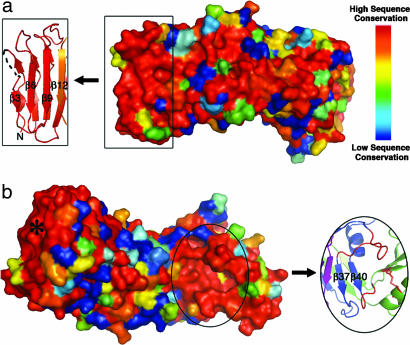
Fig. 3.
The VacA p55 structure has two patches of conserved residues. (a) The 62 m1, 27 m2, and 3 m1/m2 chimeric VacA sequences were aligned and scored with a Risler matrix according to the extent of sequence variation. Scores were displayed on the p55 structure surface with a color ramp (red, orange, yellow, green, light blue, dark blue) in which strictly conserved residues are colored red, and the most variable residues are colored dark blue. One conserved region is at the N terminus of the protein (boxed) and correlates to the β3, β6, and β9 strands of the β-helix. We propose that this surface is important for VacA oligomerization. (b) Rotation of the molecule in view a by ≈180° around the long axis of the protein reveals the second conserved region of the VacA p55 structure. This surface is located in a pocket at the C terminus of the β-helix (circled) and may represent a common receptor-binding site for all m1 and m2 VacA proteins. The pocket is formed by two long β-helix loops (red) and the disulfide bond (also in red) of the C-terminal domain. Although the asterisked region is also highly conserved, this correlates to the N terminus of the β-helix that we predict to be buried when p33 is present.