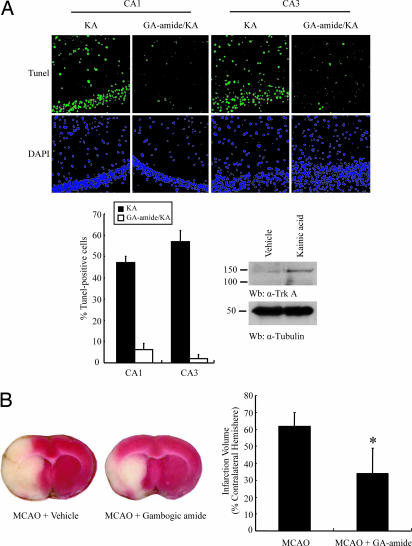
Fig. 5.
Gambogic amide prevents neuronal cell death and decreases infarct volume in MCAO animal model. (A) Gambogic amide diminished Kainic acid-triggered hippocampal neuronal cell death. The brain slides were analyzed with TUNEL assay and stained with DAPI. Green stands for apoptotic nuclei, which also were stained with DAPI. Kainic acid evidently initiated devastating apoptosis in hippocampal CA3 region, which was substantially blocked by gambogic amide (Upper). (Lower Left) Quantitative analysis of apoptosis in the hippocampal neurons. (Lower Right) KA treatment enhanced TrkA expression in hippocampus and cortex. (B) Gambogic amide reduces infarct volume in MCAO rat brain. Tetanus toxin-stained coronal section from representative animals given either vehicle or gambogic amide and had brains harvested at 24 h postocclusion. (Left) The infarct area in gambogic amide-treated animals is substantially reduced. Infarct volumes after 24 h MCAO. Compared with vehicle alone, gambogic amide significantly reduced total infarct volumes (percentage of contralateral hemisphere). (Right) The data are represented as mean ± SD; *, P < 0.05.