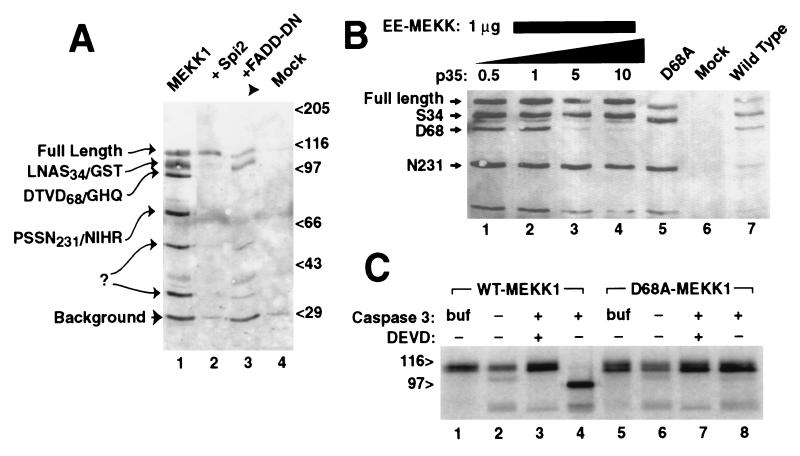
Figure 1.
MEKK1 is cleaved at amino acid D68 by caspase 3/CPP32. (A) C-terminally GST-tagged MEKK1 expressed in 293 cells demonstrated six plasmid derived bands (lane 1) detected here by glutathione precipitation and anti-GST immunoblotting. Amino terminal sequencing of these fragments confirmed proteolysis at the indicated sites, following amino acids S34, D68, and N231; two other cleavage sites were not determined. Cotransfection of either the vaccinia virus protease inhibitor Spi-2 (lane 2) or dominant negative Δ1–79 FADD (lane 3) prevented cleavage at D68 and smaller bands. (B) Cleavage of MEKK at D68 was blocked by cotransfection of increasing molar ratios of plasmid encoding baculoviral caspase inhibitor p35 (0.5–10 μg), with minimal effects on other cleavage fragments (lanes 1–4). Mutation of codon D68 of MEKK1 to alanine prevented cleavage at codon 68 (lane 5). (C) Cleavage of MEKK1 by caspase 3 in vitro. Full-length murine MEKK1, either wild-type (lanes 1–4) or mutant D68A (lanes 5–8) expressed by using in vitro transcription/translation was treated with buffer alone (lanes 1 and 5) or with extracts of untransformed bacterial cells (lanes 2 and 6), or bacterial extracts expressing active caspase 3 (lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8). Caspase 3 cleaved MEKK1, yielding a 100-kDa band. The caspase inhibitor z-DEVD-fmk blocked the cleavage (lane 3), and the D68A mutant was resistant to cleavage (lane 8).