Figure 4.
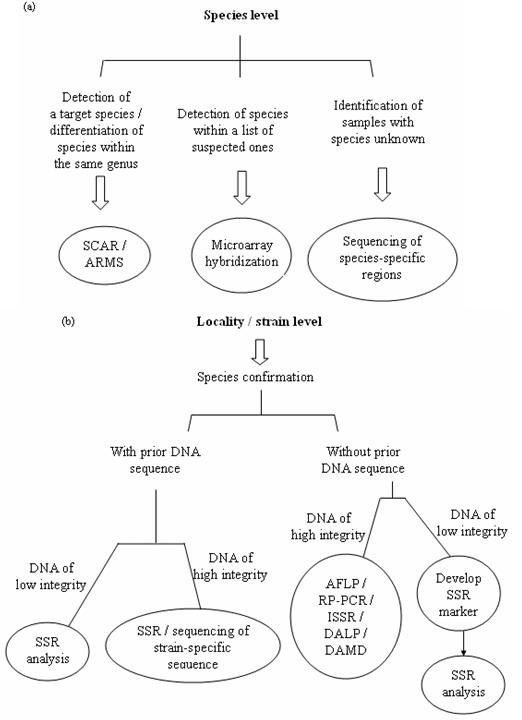
Selection of appropriate molecular identification methods for (a) species and (b) locality/strain levels. a) For species level, SCAR and ARMS are suitable for detection of a target species or differentiation of species within the same genus. Microarray hybridization is suitable for detection of species within a list of suspected ones. Sequencing of species-specific regions is suitable for identification of samples with its species totally unknown. b) For locality or strain level, species identification should be performed first. Then, depending on whether prior sequence knowledge is available and the integrity of the DNA samples, different methods can be applied. SSR analysis and sequencing of strain-specific sequences are suitable for samples with primer sequences already available and SSR analysis is especially suitable for samples with DNA of low integrity. For samples without prior sequence knowledge, SSR marker development followed by subsequent SSR analysis can be applied for DNA samples of low integrity, while AFLP, RP-PCR, ISSR, DALP and DAMD can be applied for DNA samples of high integrity.
