Figure 2.
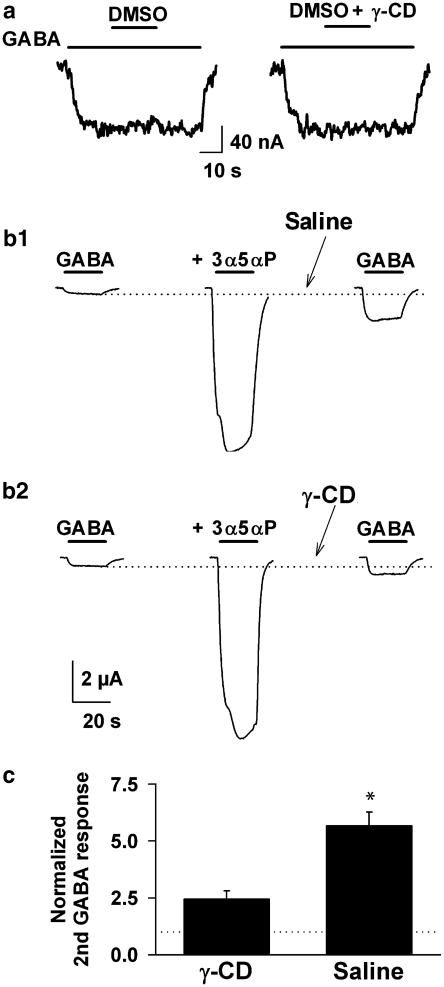
The effects of γ-cyclodextrin are induced through steroid sequestration. (a) The formation of a complex between γ-cyclodextrin and DMSO cannot explain γ-cyclodextrin effects. Neither DMSO alone nor co-application with γ-cyclodextrin affected the GABA (2 μM) responses of Xenopus oocytes expressing rat α1β2γ2L subunit combinations. (b) Cyclodextrin wash in the absence of DMSO and GABA increased recovery rate for GABA responses. (b1) Response to 2 μM GABA, and the same concentration of GABA co-applied with 10 μM 3α5αP are shown in the two left traces. The co-application trace was followed with a wash for 60 s in saline, then a re-challenge with GABA alone. Note that the response to GABA was still potentiated above the original GABA responses (dotted line). (b2) The same oocyte was re-challenged following the eventual return of the GABA response to baseline. In this case, the wash after drug application included 30 s of 0.5 mM γ-cyclodextrin followed by 30 s of plain saline. The response had been restored to much nearer the original GABA response. (c) Summary of results from six oocytes subjected to the protocol shown in (b). Wash with cyclodextrin significantly speeded recovery toward the original GABA response (* indicates P<0.05, paired t-test). The dotted line at a y-value of 1.0 indicates the original (first) GABA response, to which the other responses were normalized.