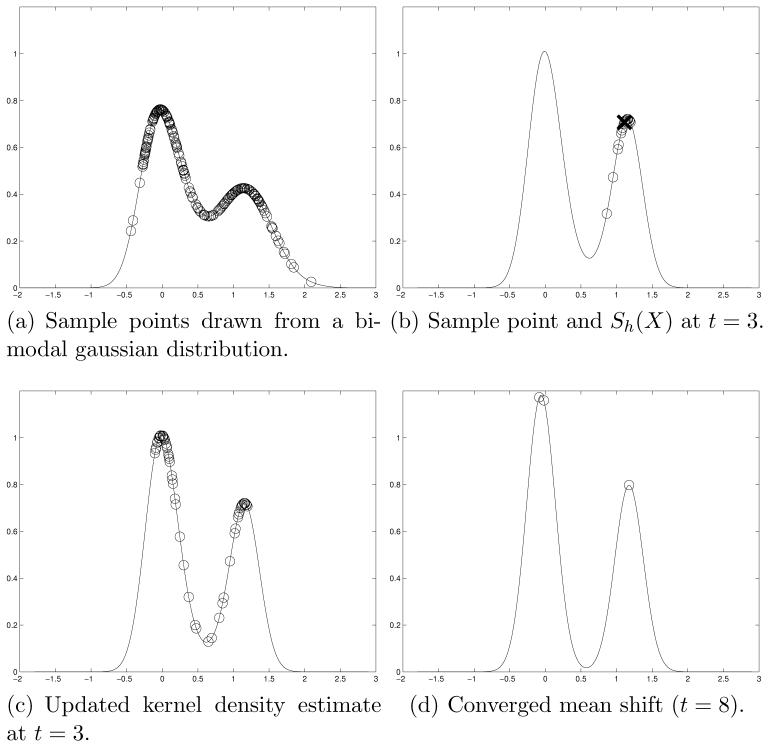
Fig. 1.
Graphical illustration of the mean shift algorithm where sample points were randomly drawn from a bi-modal mixture-of-gaussians distribution. In (a), the sample points are displayed on top of a kernel density estimate of the underlying distribution (see equation (1)). At each iteration of the mean shift, samples from the neighborhood Sh(X) are used to form the mean shift, Mh(X). This is shown in (b) for t = 3 and a sample point marked by an “X”, with the points in marked by open circles. The algorithm converges rapidly, (d) shows the updated sample points converged to the modes of the underlying distribution at t = 8. In this case, we have updated the kernel density estimate at each iteration, resulting in a narrowing of the peaks in (d).