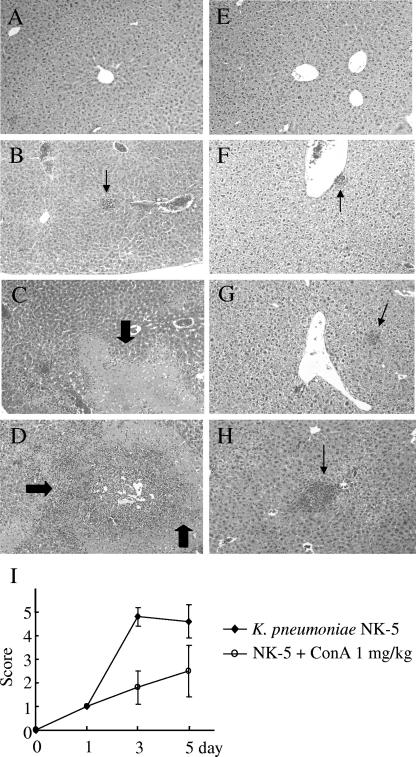
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of K. pneumoniae-induced liver damage by ConA. Groups of six to seven B6 mice were inoculated intragastrically with 2 × 108 K. pneumoniae NK-5 cells per mouse. ConA (1 mg/kg of body weight) was administrated as described for Fig. 1A. The mice were sacrificed at different times postinfection, and the liver sections were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. (A) PBS, without K. pneumoniae, day 3; (B) PBS, K. pneumoniae, day 1; (C) PBS, K. pneumoniae, day 3; (D) PBS, K. pneumoniae, day 5; (E) ConA, no K. pneumoniae, day 5; (F) ConA, K. pneumoniae, day 1; (G) ConA, K. pneumoniae, day 3; (H) ConA, K. pneumoniae, day 5. The thick arrows indicate the necrosis region; the thin arrows indicate the liver abscess. Magnification, ×400. Figure 2I indicates the degree of liver inflammation as determined by histological examination as described in Materials and Methods.