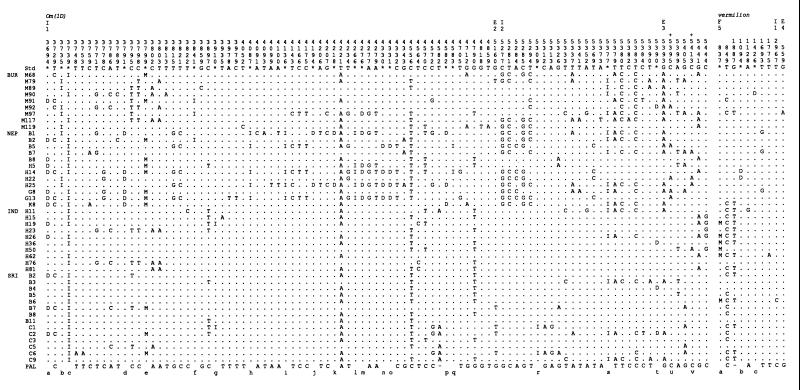
Figure 1.
DNA polymorphisms of the Om(1D) and vermilion genes found in 45 lines of D. ananassae. The localities of the strains are indicated on the far left side. The nucleotides within the reference sequence STD (from ref. 26 and as determined from a ca;px clone) are shown along the top. ∗ indicate insertions (I), deletions (D), or complex mutations (M). The numbers above the sequence represent the position numbers of each segregating site within the reference sequences, the nucleotide preceding an insertion, the start of a deletion or the nucleotide preceding a complex mutational event. The homologous nucleotides within the D. pallidosa sequences (PAL) are along the bottom. Dashes indicate where the homologous nucleotide of D. pallidosa could not be determined. Sequence domains of both genes are indicated at the top, E (exon) and I (intron), and F5 (5′ flanking region of v). + indicates amino acid replacement polymorphisms at sites 5395 and 5413 of Om(1D). Insertions, deletions, complex mutations, and amino acid changes in Om(1D) are as follows: a, 3694; b, 60 bp; c, 18 bp; d, 3791; e, TTACTA replaced by a 50-bp sequence; f, T; g, 141 bp; h, 17 bp; i, A; j, 4194 to 4205; k, 4218; l, AGA; m, 4276; n, 4330; o, 4331; p, 4582; q, T; r, T; s, G; t, 5390; u, Thr (ACC) to Asn (AAC); v, Met (AUG) to Lys (AAG). The deletions and the complex mutation in v are as follows: a, TTG replaced by ACC; b, 1094 to 1098; c, 1426 to 1434. The v sequences of D. ananassae and D. pallidosa have been submitted to GenBank (accession nos. AF028834 and AF028835, respectively).