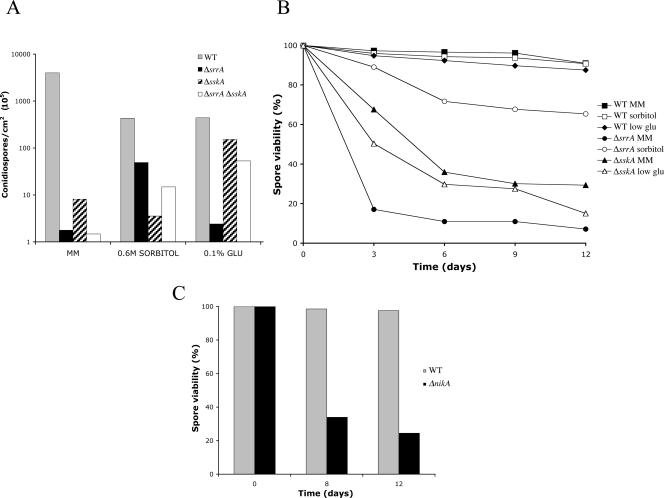
FIG. 5.
SrrA, SskA, and NikA are required for asexual sporulation and conidiospore viability. (A) Strains 11035 (wild type [WT]), TΔsrrA-pyrG7 (ΔsrrA), TΔsskA-riboB8 (ΔsskA), and TΔsrrA-pyrG/ΔsskA-riboB8 (ΔsrrA ΔsskA) were point inoculated onto supplemented MM plates or onto plates containing MM with 0.6 M sorbitol or MM with low (0.1%) glucose concentrations and were incubated at 37°C for 6 days. Total conidiospores per colony were harvested, counted, and the count divided by the colony area to obtain the number of conidiospores per square centimeter. Conidial yield data are means for two independent colonies. (B) Conidiospore suspensions from the experiment for which results are shown in panel A were plated immediately after counting or maintained at 4°C for up to 12 days. At the indicated time points, aliquots were diluted appropriately and used to inoculate supplemented MM plates, which were incubated at 37°C for 2 days; then colonies were counted. (C) Strains CLK43 (WT) and CIVΔnikA3 (ΔnikA) were point inoculated onto supplemented MM plates and incubated at 37°C for 6 days. Conidia were collected, counted, divided by the colony area, and treated as for panel B. For panels B and C, the number of germinated spores at the time of harvesting was considered as 100% viability for each strain. The number of colonies counted ranged from 127 to 214 per plate. Data shown are means for two independent plates, showing a maximum variation of 17% with respect to the mean.