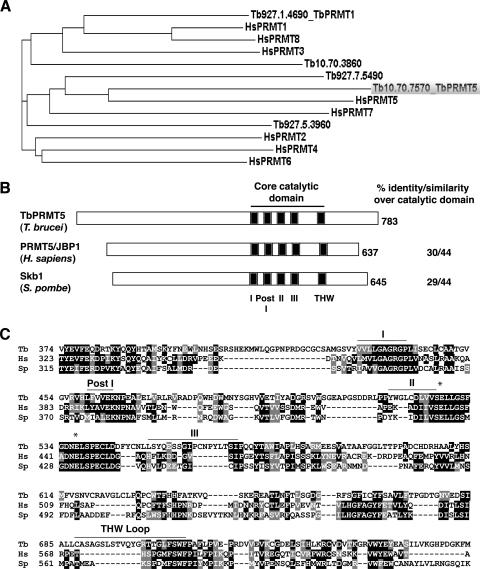
FIG. 1.
TbPRMT5 is a putative type II PRMT with a conserved methyltransferase domain. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of putative PRMTs identified in T. brucei with PRMT homologs from H. sapiens. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using the ClustalW multiple-sequence alignment tool. The GenBank accession numbers are as follows: HsPRMT1, NP_001527; HsPRMT2, NP_001526; HsPRMT3, NP_005779; HsPRMT4, NP_954592; HsPRMT5, O14744; HsPRMT6, Q96LA8; HsPRMT7, NP_061896; and HsPRMT8, Q9NR22. (B) Schematic representation of PRMT5 homologs from T. brucei (TbPRMT5), H. sapiens (PRMT5/JBP1; GenBank accession no. O14744), and S. pombe (Skb1; GenBank accession no. P78963) illustrating the presence of a conserved methyltransferase domain (motifs I, Post I, II, and III) and variable N termini. The percent amino acid identity/similarity over the core catalytic domain (278 amino acids in TbPRMT5) is shown. (C) A multiple-sequence alignment of core catalytic domains and flanking regions of the PRMTs shown in panel B was generated using ClustalW. Similar amino acids are shaded gray, while identical amino acids are shaded black. The conserved AdoMet binding domain (motifs I, Post I, II, and III) is indicated above the sequences. The double-E loop is denoted with asterisks. The THW domain is denoted with a bar and does not appear to be conserved in type II PRMTs. Tb, T. brucei; HS, H. sapiens; Sp, S. pombe.