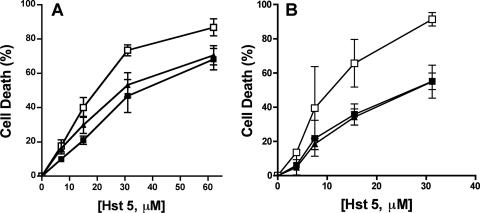
FIG. 3.
C. albicans cells with an impaired oxidative-stress response are more sensitive to high doses of Hst 5. C. albicans oxidative-stress response pathways were tested for their sensitivities to Hst 5 killing. (A) Cells with inactivation of the transcriptional regulatory protein required for oxidative-stress tolerance independent of Hog1 were tested using a wild-type strain (filled squares), a cap1/cap1 deletion mutant (open squares), and a single-allele CAP1/cap1 strain (filled triangles). (B) The Sln1 branch of the HOG pathway was tested by comparing ssk1/ssk1 cells (open squares) with wild-type CAF2-1 (filled squares) and SSK1/ssk1 (filled triangles) cells. Cells were treated with 3.8 to 62 μM Hst 5 for 1 h at 30°C, and loss of cell viability is expressed as [1 − (colonies after Hst 5 treatment/colonies after incubation with buffer only)] × 100. Both C. albicans cap1/cap1 and ssk1/ssk1 strains showed significantly (P < 0.05) more sensitivity to Hst 5 only at higher dosages (31 μM and 62 μM).