FIGURE 2. Secondary structure of rhodopsin mapped with stable structural segments.
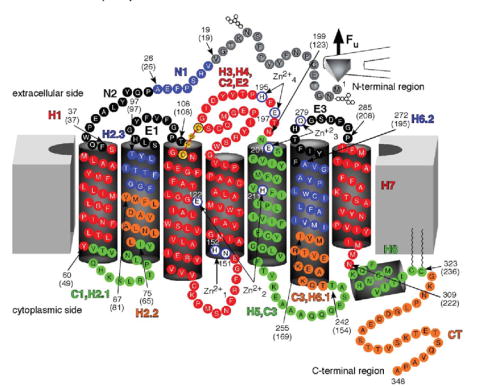
Values from WLC model fitting (Table 1, Fig. 1) were used to estimate the location of stable structural segments in the secondary structure of rhodopsin. Each stable structural segment and its name is colored differently. Arrows indicate the start and end of each structural segment, and the corresponding amino acid residue number is indicated. Numbers in brackets are the values obtained from WLC model fits, which indicate the number of amino acid residues stretched above the membrane. Zn2+-binding sites observed in crystal structures of rhodopsin are shown in white. Amino acid residues that coordinate Zn2+ at those sites are as follows: , Asn151 and His152; , Glu122 and His211; , Glu201 and Gln279; , Glu197 and His195.
