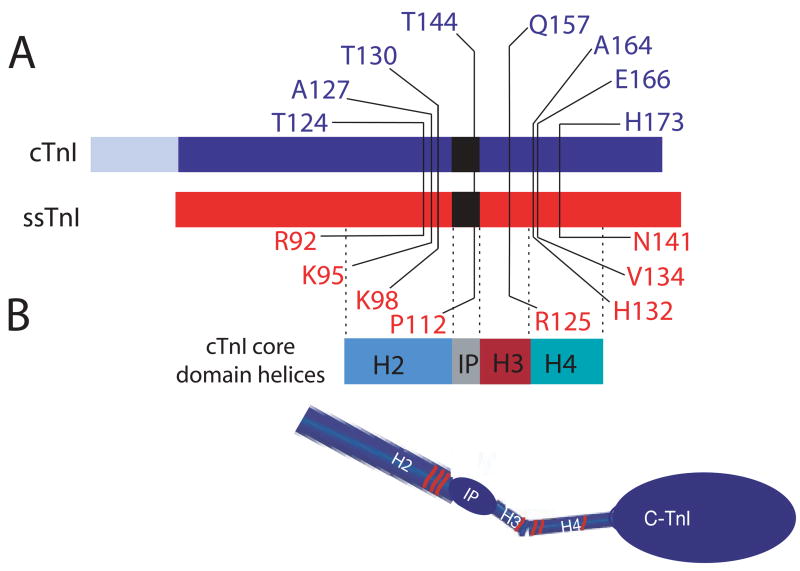
FIGURE 1.
A. Illustration of amino acid substitutions within cardiac (blue) and slow skeletal troponin I (red). B. The core domain helices (2) are identified below the linear diagram of the troponin I isoforms, and a model of the core domain is shown below the linear diagram for each troponin I to demonstrate the location of these mutations within the defined 3-dimensional structure of TnI. The R125Q mutation lies within the H3 helical domain, while the H132A (cTnIA164H), V134E, and N141H in ssTnI are located in the H4 helix defined by Takeda et al. (2). The ssTnIQAE mutant contains all 3 of these substitutions, and ssTnIR92T, K95A, and K98T were used to construct additional substitution mutants for ssTnIQAETAT. The last 3 substitutions are all located within the H2 helical domain. The cTnIT144P and ssTnIP112T substitution mutants are located within the inhibitory peptide (IP) region of TnI.