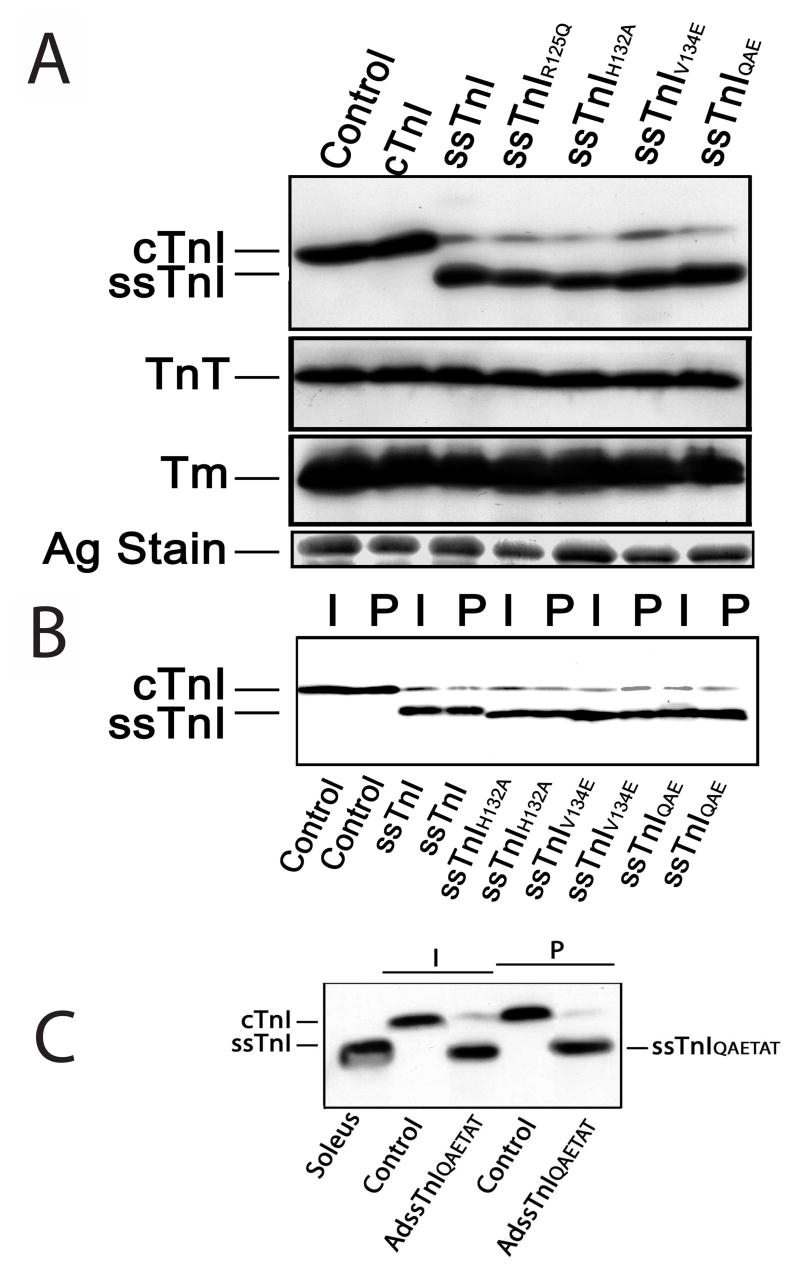
FIGURE 2.
Expression and myofilament incorporation of ssTnI and the substitutions constructed within ssTnI. A. Representative Western blot analysis of cardiac (cTnI) and slow skeletal TnI (ssTnI) expression in myocytes 6 days after gene transfer of wildtype ssTnI, ssTnIR125Q, ssTnIH132A, ssTnIV134E, or ssTnIQAE and in non-infected controls (control). Expression of the thin filament proteins tropomyosin (Tm) and troponin T (TnT), and a silver stained (Ag stain) portioned of the gel are also included here. Composite results for relative expression of TnI, TnT and Tm are shown in Table 2. B. Representative expression before (intact; I) and after (permeabilized; P) detergent permeabilization of non-infected control myocytes and myocytes expressing ssTnI substitution mutants shown in A. These results demonstrate TnI expressed after gene transfer is incorporated into the myofilament and does not accumulate in the cytosol. Composite results for expression of substitution mutants in intact and permeabilized myocytes are shown in Table 1. C. Representative Western blot analyses of ssTnIQAETAT expression in intact (I) and detergent-permeabilized (P) myocytes 6 days after gene transfer. Labels shown below the figure indicate source of muscle (soleus), control myocytes or myocytes after gene transfer with adenoviral vector (AdssTnIQAETAT).