Fig. 1.
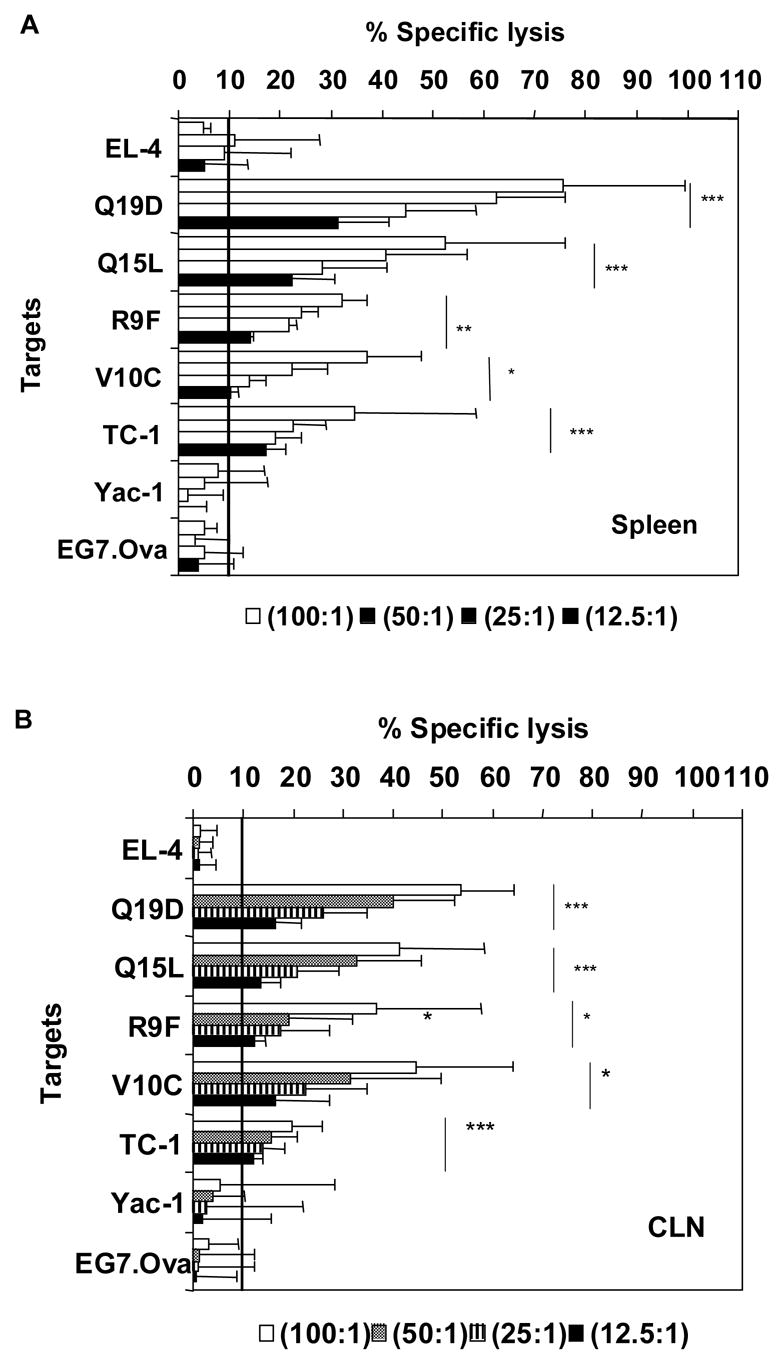
Intranasal immunization with the mixture of E744–62 (Q19D) and E643–57 (Q15L) peptides from HPV-16 using the mutant cholera toxin (CT-2*) adjuvant induces CTL responses. C57Bl/6 mice were immunized by the intranasal route with peptides Q19D and Q15L (100 μg each) and CT-2* (1 μg) a total of 2 times at 5 day intervals. Cells isolated from the spleen and cervical lymph nodes (CLN) were restimulated for 5 days in vitro with Q19D and Q15L peptides before assaying for CTL activity. (A) The restimulated spleen cells (panel A) and CLN (panel B) were tested for CTL activity against MHC-matched EL-4 target cells pulsed with Q19D, R9F, Q15L or V10C peptides or TC-1 tumor cells. The 51Cr-labelled TC-1 cells were mixed with unlabelled YAC-1 cells that serve as targets for NK activity, to determine the tumor-cell-specific lysis. The EG7.Ova tumor targets expressing Ova protein served as negative control target cells for ascertaining the antigen specific lysis of the TC-1 cells. The horizontal line in each panel indicates the cut-off value for positive response (10% antigen-specific lysis). Data shown is an average of at least three separate experiments. Student t-test analysis was done by comparing with the EL-4 empty targets to determine the p values. Values ≤ 0.00005 have been assigned = ***, p ≤ 0.0005 = ** and p ≤ 0.005 = *.
