Fig. 2.
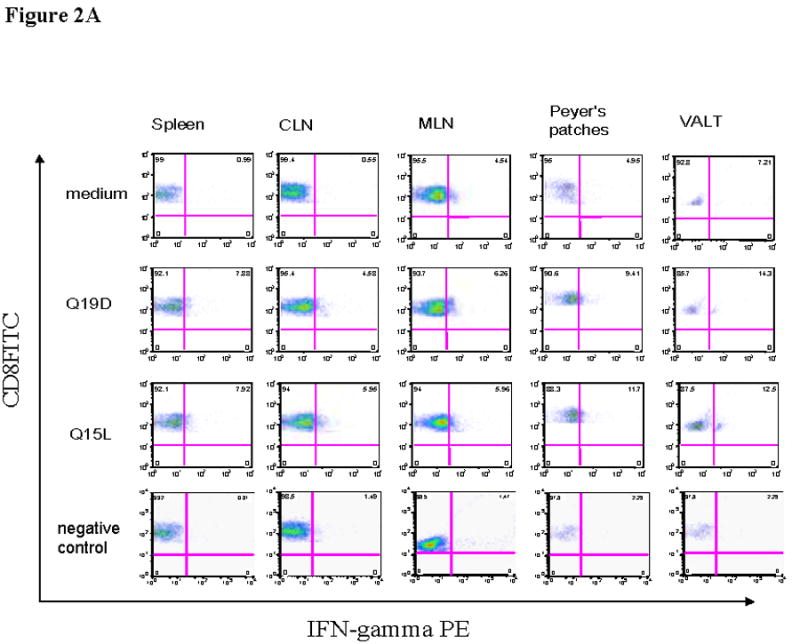
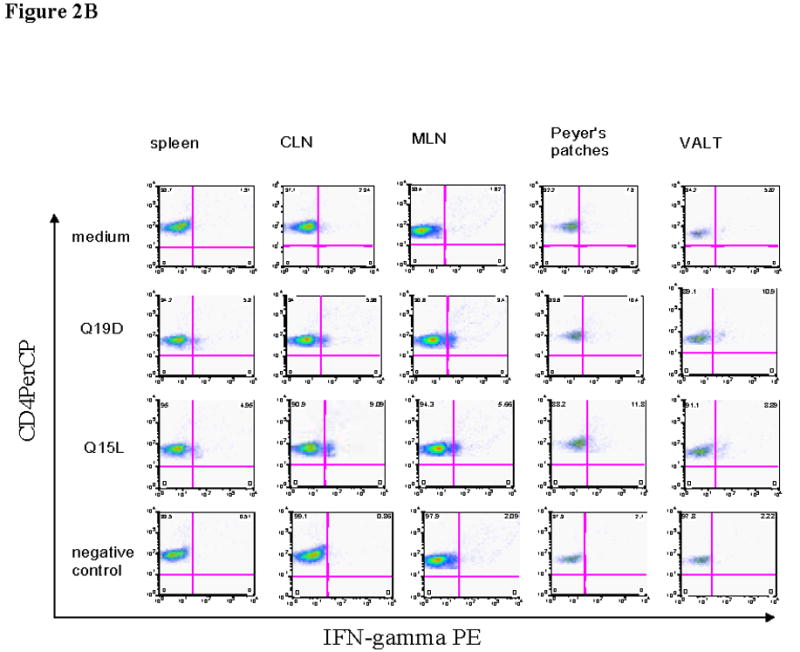
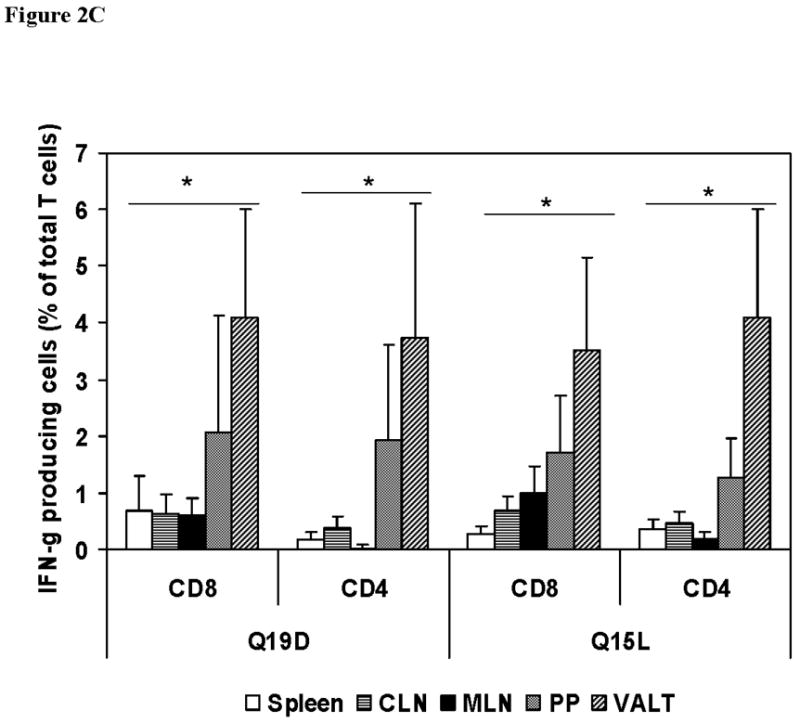
Intranasal immunization with the mixture of E744–62 (Q19D) and E643–57 (Q15L) peptides from HPV-16 using the mutant cholera toxin (CT-2*) adjuvant primes antigen-specific IFN-γ production by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Cells isolated from various mucosal and systemic tissues of C57BL/6 mice immunized by the intranasal route with mixture of Q19D and Q15L peptides were stimulated in vitro using medium cognate peptides or a non-specific negative control peptide individually (2μg/ml) for determining the IFN-γ producing in (A) CD8+ and (B) CD4+ T cells. Cells were stained for CD3, CD4 and CD8 surface markers and for intracellular IFN-γ as described in the methods section. The numbers of IFN-γ-producing T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry and the percentages of CD8+/IFN-γ+ CD4+/IFN-γ+ (double-positive) T cells are shown in the upper right corner of each dot plot. The data shown is one representative of 5 separate experiments performed. (C) the bar graph shows the average values along with standard errors of percentages of CD8+/IFN-γ+ CD4+/IFN-γ+ (double-positive) T cells in 1 ×106 cells specific to peptides Q19D and Q15L in spleen, CLN, MLN, peyer’s patches and VALT. The p values were determined by comparing with medium alone and values ≤ 0.05 (*) are considered significant.
