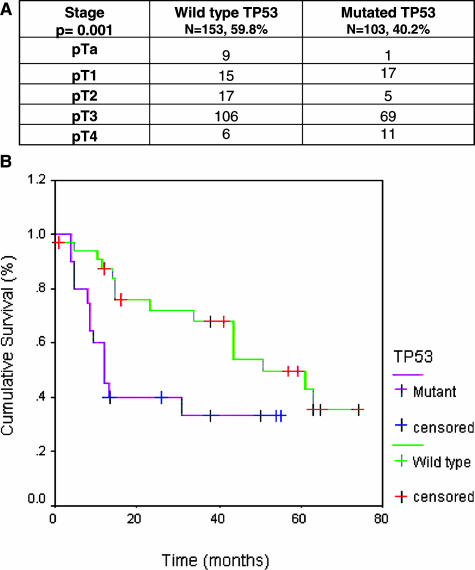
Figure 2.
A: Distribution of wild-type and mutated TP53 status along bladder cancer progression. An increased altered TP53 was observed in advanced disease compared with non-muscle-invasive bladder lesions. TP53 genotype status was found significantly associated with tumor stage (Kruskall-Wallis, P = 0.001). B: Association of TP53 status with clinical outcome. Overall survival of patients with bladder cancer and mutant TP53 was significantly shorter than those presenting a wild-type TP53 genotype (log-rank, P = 0.01).