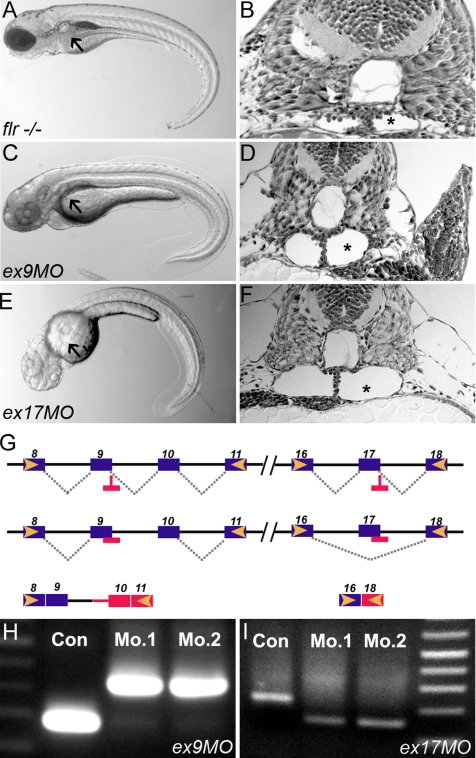
Figure 3.
Antisense morpholinos targeting the fleer candidate phenocopy the flrm477 mutant. (A) flr−/− embryos exhibit axis curvature and bilateral pronephric cysts (arrows). (B) Histological section of flr mutant showing tangential section of pronephric cyst (asterisk). (C) Embryos injected with morpholinos targeting the splice donor sites in flr exon 9 exhibit kidney cysts and axis curvature identical to flrm477. (D) Histology of the pronephric region in flr exon 9 morphant showing cyst formation. (E) Exon 17 morphants show cystic distention (asterisk) within the pronephros. (G) Summary of molecular defects caused by morpholino targeting of splice donor sites at exon 9 and 17. (H) RT-PCR analysis using primers flanking the exon 9 show an increase in amplicon size due to inclusion of intron 9 in the altered mRNA. (I) RT-PCR analysis using primers flanking the exon 17 shows a decrease in amplicon size due to exon 17 skipping. Analysis of two different single morphant larvae for each morpholino demonstrates reproducibility of flr knockdown.