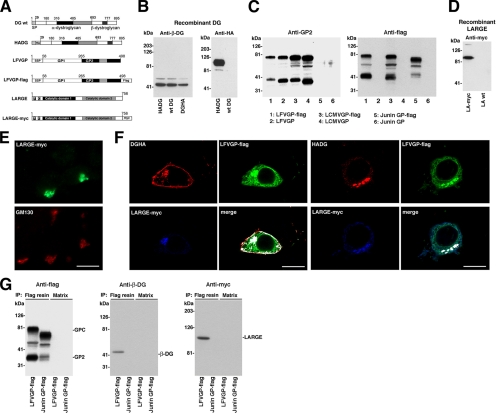
Figure 7.
The viral GP associates with DG and LARGE. (A) Schematic representation of the tagged protein variants: The N-terminal domain of α-DG is shown in white, the mucin-type central domain in black, and the C-terminal globular domain in gray. β-DG and the HA epitope are indicated. LFVGP is depicted analogous to LCMVGP in Figure 6A with the C-terminal flag epitope indicated. The two putative catalytic domains of LARGE are shown in black and gray, respectively, followed in LARGE-myc by a C-terminal myc epitope. (B) Expression of wild-type DG, HADG, and DGHA: HEK293T cells were transfected with wild-type DG, HADG, and DGHA. After 48 h, total cell protein was extracted and probed in Western blot for β-DG and HA epitope. Molecular masses are indicated. (C) Expression of wild-type and C-terminally flagged viral GPs: wild-type LCMVGP cl-13, LFVGP, and Junin GP and the tagged versions LCMVGP cl-13-flag, LFVGP-flag, Junin GP-flag, and GFP were expressed in HEK293T cells, and total cell protein was examined by Western blot by using mAb 83.6 anti-GP2 and a mAb anti-flag. Note that mAb 83.6 does not recognize Junin GP in Western blot. (D) Wild-type and C-terminally tagged LARGE (LARGE-myc) were expressed in HEK293T cells, and total cell protein was probed with an anti-myc antibody. (E) Cellular localization of LARGE-myc: LARGE-myc was transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. After 48 h, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with a rabbit polyclonal antibody to myc epitope and a mouse mAb to the Golgi marker GM130. Primary antibodies were detected with secondary antibodies to mouse and rabbit IgG conjugated to FITC (green) and Rhodamine Red-X (red), respectively. Bar, 10 μm. (F) Colocalization of DG, LFVGP, and LARGE: HEK293T cells were cotransfected with the DG variant indicated, together with LFVGP-flag and LARGE-myc. After 48 h, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and costained with mouse mAb F7 to HA epitope (DGHA, HADG), polyclonal rabbit anti-myc antibody (LARGE-myc), and a polyclonal goat anti-flag antibody (LFVGP-flag). Primary antibodies were detected with secondary antibodies anti-mouse IgG-Rhodamine Red-X (red), anti-goat IgG-FITC (green), and anti-rabbit IgG-Cy5 (blue). Confocal images were acquired as in Figure 6C. Colocalization is white in the merged images. (G) LFVGP associated with LARGE in a molecular complex: HEK293T cells were cotransfected with either LFVGP-flag or Junin GP-flag and LARGE-myc. After 48 h, cells were lysed and cleared cell lysates subjected to IP with either mAb M2 anti-FLAG conjugated to Sepharose (flag resin) or control Sepharose matrix (matrix). Immunocomplexes were separated by SDS-PAGE. Flag-tagged GPs were detected with a polyclonal rabbit antibody to flag (anti-flag). β-DG was detected with biotinylated mAb 8D5 (Anti-β-DG) and streptavidin-HRP. LARGE-myc was probed with a rabbit polyclonal anti-myc antibody (anti-myc). Molecular masses and the positions of GPC, GP2, β-DG, and LARGE are indicated.