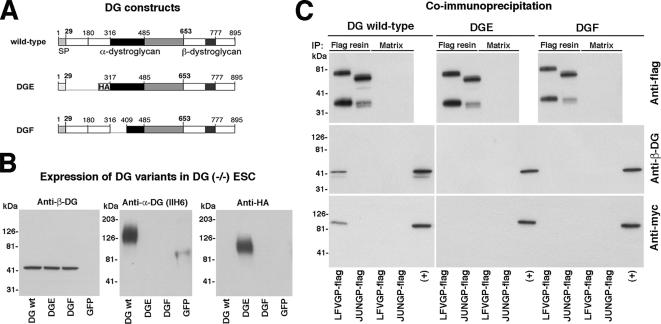
Figure 9.
The LARGE binding site and substrate site on α-DG are required for the association of LFVGP with LARGE. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type DG, DGE (Δ30-316), and DGF (Δ317-408) with DG domains depicted as in Figure 7A. (B) α-DG derived from DGE and DGF lacks functional glycosylation. Wild-type DG, DGE, DGF, and GFP were expressed in DG (−/−) ES cells by using AdV vectors. After 48 h, WGA affinity purification was performed, and eluted glycoprotein was probed in Western blot with polyclonal antibody AP83 to β-DG, mAb IIH6, and an anti-HA antibody. (C) CoIP of LFVGP with DG and LARGE. DG (−/−) ES cells were cotransfected with flag-tagged GPs of LFV or Junin and LARGE-myc, followed by AdV-mediated gene transfer of wild-type DG, DGE, or DGF. After total 48 h, cell lysates were prepared, and coIP performed as described in Figure 8B. Immune complexes were separated and probed with polyclonal antibody to flag-tag (anti-flag), polyclonal antibody AP83 to β-DG (anti-β-DG), and polyclonal antibody to myc tag (anti-myc). Positive control lanes (+) correspond to samples of total cell lysates to verify the presence of the indicated proteins.