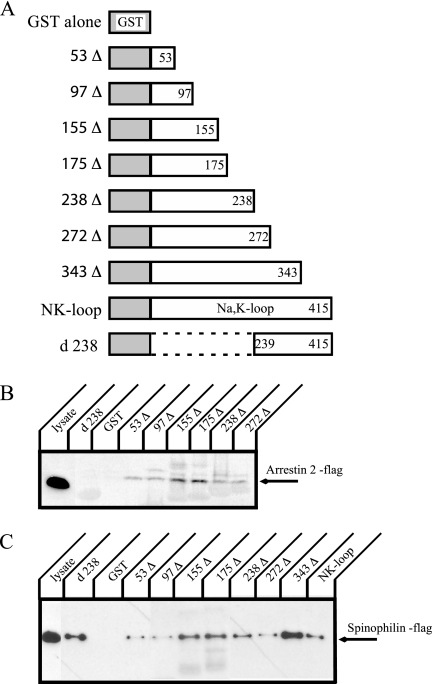
Figure 3.
Truncation constructs of the large cytoplasmic loop of the Na+,K+-ATPase α-subunit and GST pulldown of arrestin 2 and spinophilin. (A) Schematic representations of the GST fusion protein constructs incorporating various deletions in the large cytoplasmic loop of the Na+,K+-ATPase α-subunit. Δs correspond to the C-terminal deletions, whereas d238 is the N-terminal deletion of the large cytoplasmic loop. The numbers refer to the residues that correspond to the C-terminal ends or, in the case of the d238 construct, the N-terminal end, of the pump sequence in the GST construct. (B) Flag-tagged arrestin 2 was expressed in COS cells, and cell lysate was incubated with GST fusion proteins. Arrestin 2 was detected by Western blot with anti-flag antibody. The 53 amino acids at the extreme N-terminal end of the large cytoplasmic loop of the Na+,K+-ATPase α-subunit appear to be sufficient for binding with arrestin 2. (C) Flag-tagged spinophilin was expressed in COS cells, and cell lysates were incubated with GST fusion proteins. Spinophilin was detected by Western blot with anti-flag antibody. Spinophilin appears to interact with at least two binding sites in the large cytoplasmic loop. Typical results from one of four experiments are shown.