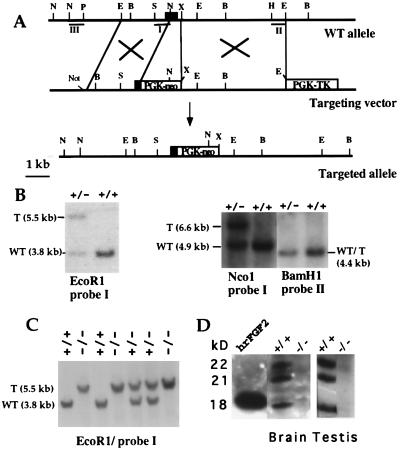
Figure 1.
FGF2 gene targeting. (A) Partial map of the FGF2 gene (Top), gene-targeting vector (Middle), and FGF2-targeted allele (Bottom). The first exon of the FGF2 gene is shown as a black box. The neo- and hsvTK-expressing cassettes, containing the PGK-1 promoter and polyadenylation sequences, are shown as white boxes. The position of the relevant restriction sites for the enzymes BamHI (B), EcoRI (E), XbaI (X), NcoI (N), SalI (S), HindIII (H), and PstI (P) is marked. The NotI site was used to linearize the targeting vector. DNA fragments I, II, and III were used as probes in Southern blot hybridization. (B) Genomic DNA from ES cells was digested with EcoRI, NcoI, and BamHI and hybridized to the probes indicated. T, targeted allele. (C) Southern blot of tail DNA from the offspring of heterozygous FGF2+/− mutant parents. DNA was digested with EcoRI and probed with probe I. (D) Absence of FGF2 in protein extracts from brain and testis of FGF2 −/− mice. Western blots of protein extracts concentrated on heparin-Sepharose beads. Blots were probed with a monoclonal anti-FGF-2 antibody (Transduction Laboratories). The same result was obtained with polyclonal antibodies for FGF2. The position of the three isoforms of FGF2 is indicated; 25 ng of human recombinant FGF2 was loaded as a control.