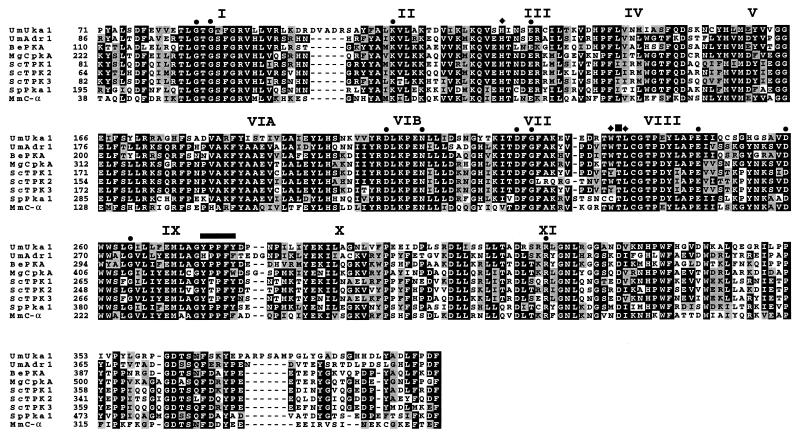
Figure 1.
Amino acid sequence alignments of the two U. maydis PKA catalytic subunits Adr1 and Uka1 with fungal and mouse catalytic subunits of PKA. Amino acid identity (black boxes) and similarity (gray boxes) are shown within the protein kinase domain (C-terminal 80%). The 11 subdomains of the protein kinase catalytic domain are indicated with roman numerals, and the twelve most highly conserved residues are highlighted with filled circles (12). Filled diamonds indicate the three residues shown to be required for the association between catalytic and regulatory subunits of PKA (18). The autophosphorylation site is indicated with a filled square. The thick horizontal line shows residues implicated in binding of the PKI substrate (19). Be, B. emersonii (20); Mg, M. grisea (21); Sc, S. cerevisiae (22); Sp, S. pombe (23); Mm, Mus musculus (24). Sequences were aligned with the clustal w (1.60) program (25).